Vol. 3A 11-23
MEMORY CACHE CONTROL
•
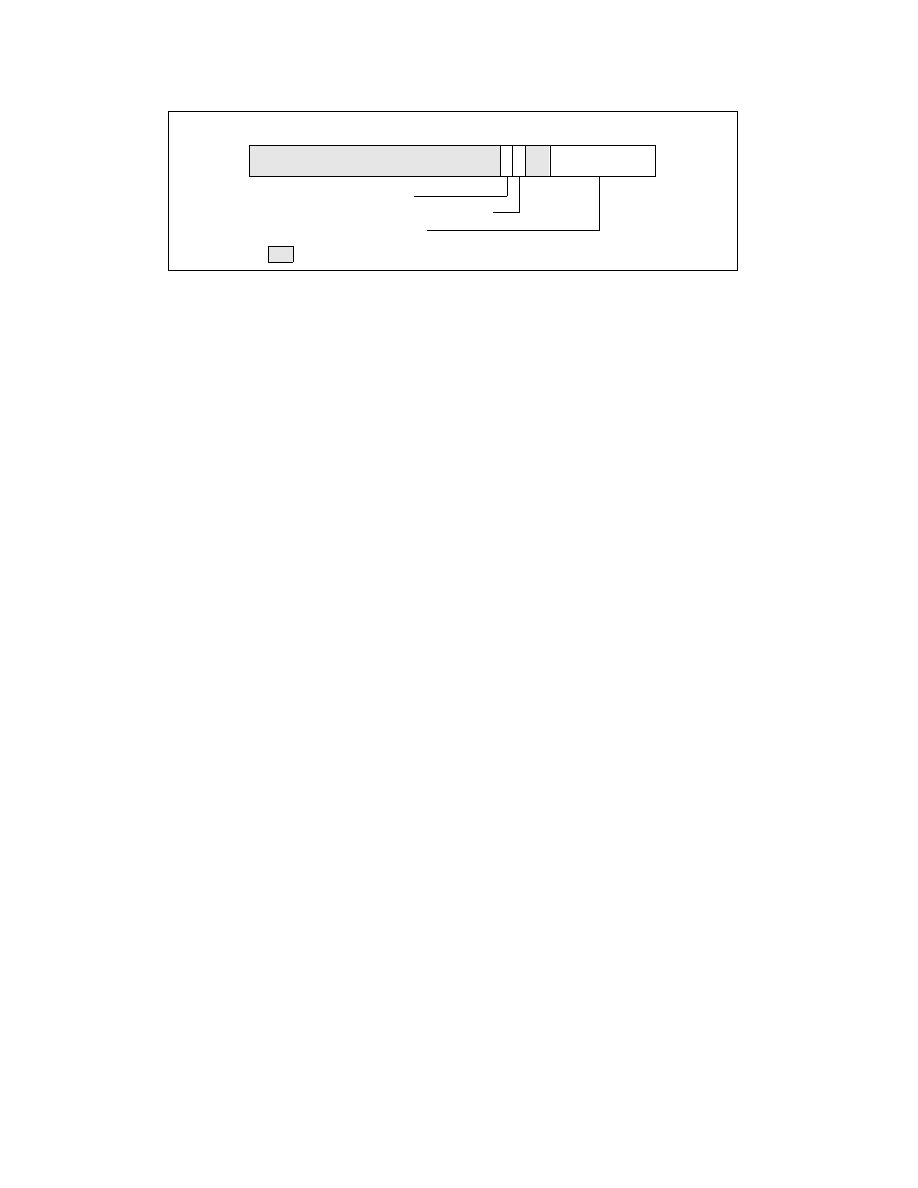
FE (fixed MTRRs enabled) flag, bit 10 — Fixed-range MTRRs are enabled when set; fixed-range MTRRs are
disabled when clear. When the fixed-range MTRRs are enabled, they take priority over the variable-range
MTRRs when overlaps in ranges occur. If the fixed-range MTRRs are disabled, the variable-range MTRRs can
still be used and can map the range ordinarily covered by the fixed-range MTRRs.
•
E (MTRRs enabled) flag, bit 11 — MTRRs are enabled when set; all MTRRs are disabled when clear, and the
UC memory type is applied to all of physical memory. When this flag is set, the FE flag can disable the fixed-
range MTRRs; when the flag is clear, the FE flag has no affect. When the E flag is set, the type specified in the
default memory type field is used for areas of memory not already mapped by either a fixed or variable MTRR.
Bits 8 and 9, and bits 12 through 63, in the IA32_MTRR_DEF_TYPE MSR are reserved; the processor generates a
general-protection exception (#GP) if software attempts to write nonzero values to them.
11.11.2.2 Fixed Range MTRRs
The fixed memory ranges are mapped with 11 fixed-range registers of 64 bits each. Each of these registers is
divided into 8-bit fields that are used to specify the memory type for each of the sub-ranges the register controls:
•
Register IA32_MTRR_FIX64K_00000 — Maps the 512-KByte address range from 0H to 7FFFFH. This range
is divided into eight 64-KByte sub-ranges.
•
Registers IA32_MTRR_FIX16K_80000 and IA32_MTRR_FIX16K_A0000 — Maps the two 128-KByte
address ranges from 80000H to BFFFFH. This range is divided into sixteen 16-KByte sub-ranges, 8 ranges per
register.
•
Registers IA32_MTRR_FIX4K_C0000 through IA32_MTRR_FIX4K_F8000 — Maps eight 32-KByte
address ranges from C0000H to FFFFFH. This range is divided into sixty-four 4-KByte sub-ranges, 8 ranges per
register.
Table 11-9 shows the relationship between the fixed physical-address ranges and the corresponding fields of the
fixed-range MTRRs; Table 11-8 shows memory type encoding for MTRRs.
For the P6 family processors, the prefix for the fixed range MTRRs is MTRRfix.
11.11.2.3 Variable Range MTRRs
The Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 family processors permit software to specify the memory type for m variable-
size address ranges, using a pair of MTRRs for each range. The number m of ranges supported is given in bits 7:0
of the IA32_MTRRCAP MSR (see Figure 11-5 in Section 11.11.1).
The first entry in each pair (IA32_MTRR_PHYSBASEn) defines the base address and memory type for the range;
the second entry (IA32_MTRR_PHYSMASKn) contains a mask used to determine the address range. The “n” suffix
is in the range 0 through m–1 and identifies a specific register pair.
For P6 family processors, the prefixes for these variable range MTRRs are MTRRphysBase and MTRRphysMask.
Figure 11-6. IA32_MTRR_DEF_TYPE MSR
Type — Default memory type
FE — Fixed-range MTRRs enable/disable
E — MTRR enable/disable
63
0
Reserved
F
E
7
10
11
Type
8
9
12
E
Reserved