Vol. 3A 11-21
MEMORY CACHE CONTROL
11.11.1 MTRR Feature Identification
The availability of the MTRR feature is model-specific. Software can determine if MTRRs are supported on a
processor by executing the CPUID instruction and reading the state of the MTRR flag (bit 12) in the feature infor-
mation register (EDX).
If the MTRR flag is set (indicating that the processor implements MTRRs), additional information about MTRRs can
be obtained from the 64-bit IA32_MTRRCAP MSR (named MTRRcap MSR for the P6 family processors). The
IA32_MTRRCAP MSR is a read-only MSR that can be read with the RDMSR instruction. Figure 11-5 shows the
contents of the IA32_MTRRCAP MSR. The functions of the flags and field in this register are as follows:
Table 11-8. Memory Types That Can Be Encoded in MTRRs
Memory Type and Mnemonic
Encoding in MTRR
Uncacheable (UC)
00H
Write Combining (WC)
01H
Reserved*
02H
Reserved*
03H
Write-through (WT)
04H
Write-protected (WP)
05H
Writeback (WB)
06H
Reserved*
7H through FFH
NOTE:
* Use of these encodings results in a general-protection exception (#GP).
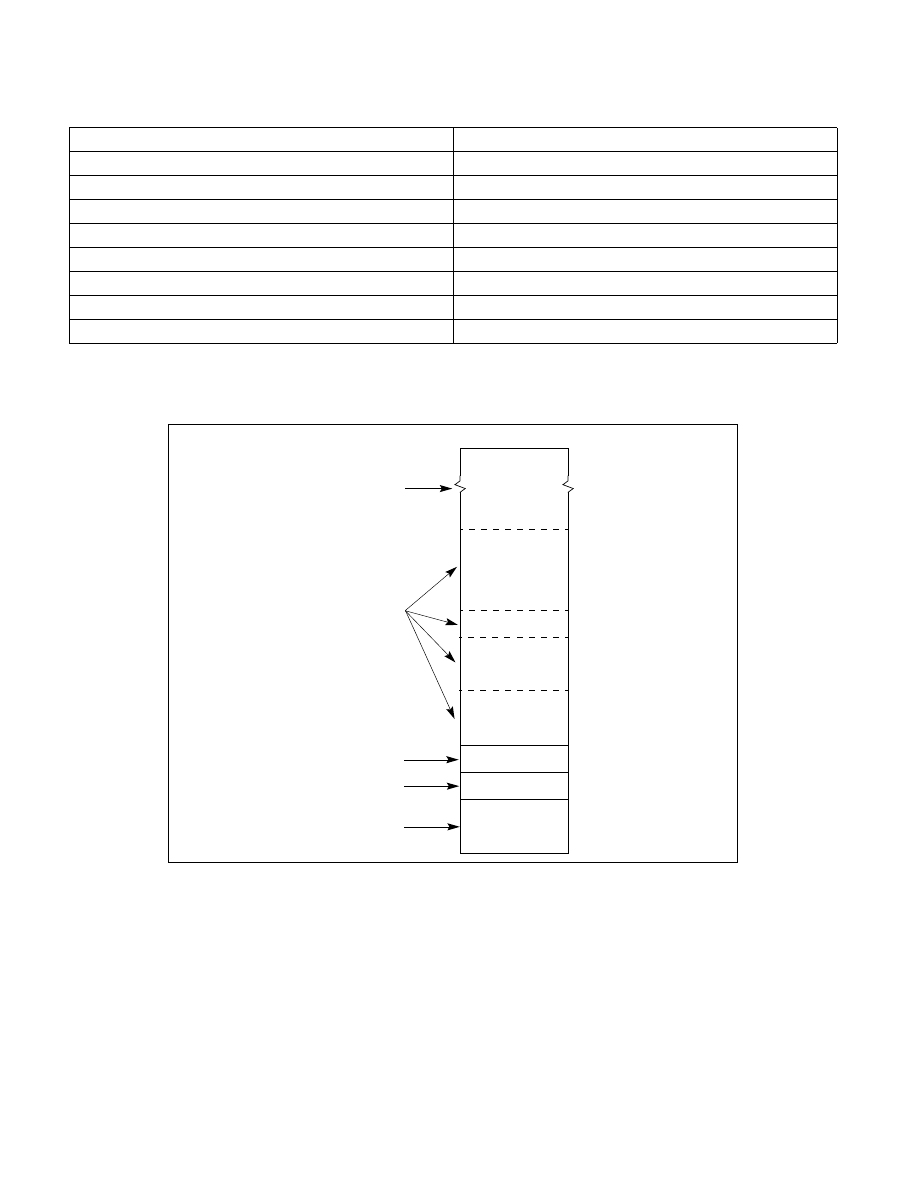
Figure 11-4. Mapping Physical Memory With MTRRs
0
FFFFFFFFH
80000H
BFFFFH
C0000H
FFFFFH
100000H
7FFFFH
512 KBytes
256 KBytes
256 KBytes
8 fixed ranges
16 fixed ranges
64 fixed ranges
Variable ranges
(64-KBytes each)
(16 KBytes each)
(4 KBytes each)
(from 4 KBytes to
maximum size of
Address ranges not
Physical Memory
mapped by an MTRR
are set to a default type
physical memory)