4-14 Vol. 3A
PAGING
4.4.2
Linear-Address Translation with PAE Paging
PAE paging may map linear addresses to either 4-KByte pages or 2-MByte pages. Figure 4-5 illustrates the trans-
lation process when it produces a 4-KByte page; Figure 4-6 covers the case of a 2-MByte page. The following items
describe the PAE paging process in more detail as well has how the page size is determined:
•
Bits 31:30 of the linear address select a PDPTE register (see Section 4.4.1); this is PDPTEi, where i is the value
of bits 31:30.
1
Because a PDPTE register is identified using bits 31:30 of the linear address, it controls access
to a 1-GByte region of the linear-address space. If the P flag (bit 0) of PDPTEi is 0, the processor ignores bits
63:1, and there is no mapping for the 1-GByte region controlled by PDPTEi. A reference using a linear address
in this region causes a page-fault exception (see Section 4.7).
•
If the P flag of PDPTEi is 1, 4-KByte naturally aligned page directory is located at the physical address specified
in bits 51:12 of PDPTEi (see Table 4-8 in Section 4.4.1). A page directory comprises 512 64-bit entries (PDEs).
A PDE is selected using the physical address defined as follows:
— Bits 51:12 are from PDPTEi.
— Bits 11:3 are bits 29:21 of the linear address.
— Bits 2:0 are 0.
Because a PDE is identified using bits 31:21 of the linear address, it controls access to a 2-Mbyte region of the
linear-address space. Use of the PDE depends on its PS flag (bit 7):
•
If the PDE’s PS flag is 1, the PDE maps a 2-MByte page (see Table 4-9). The final physical address is computed
as follows:
— Bits 51:21 are from the PDE.
— Bits 20:0 are from the original linear address.
•
If the PDE’s PS flag is 0, a 4-KByte naturally aligned page table is located at the physical address specified in
bits 51:12 of the PDE (see Table 4-10). A page table comprises 512 64-bit entries (PTEs). A PTE is selected
using the physical address defined as follows:
— Bits 51:12 are from the PDE.
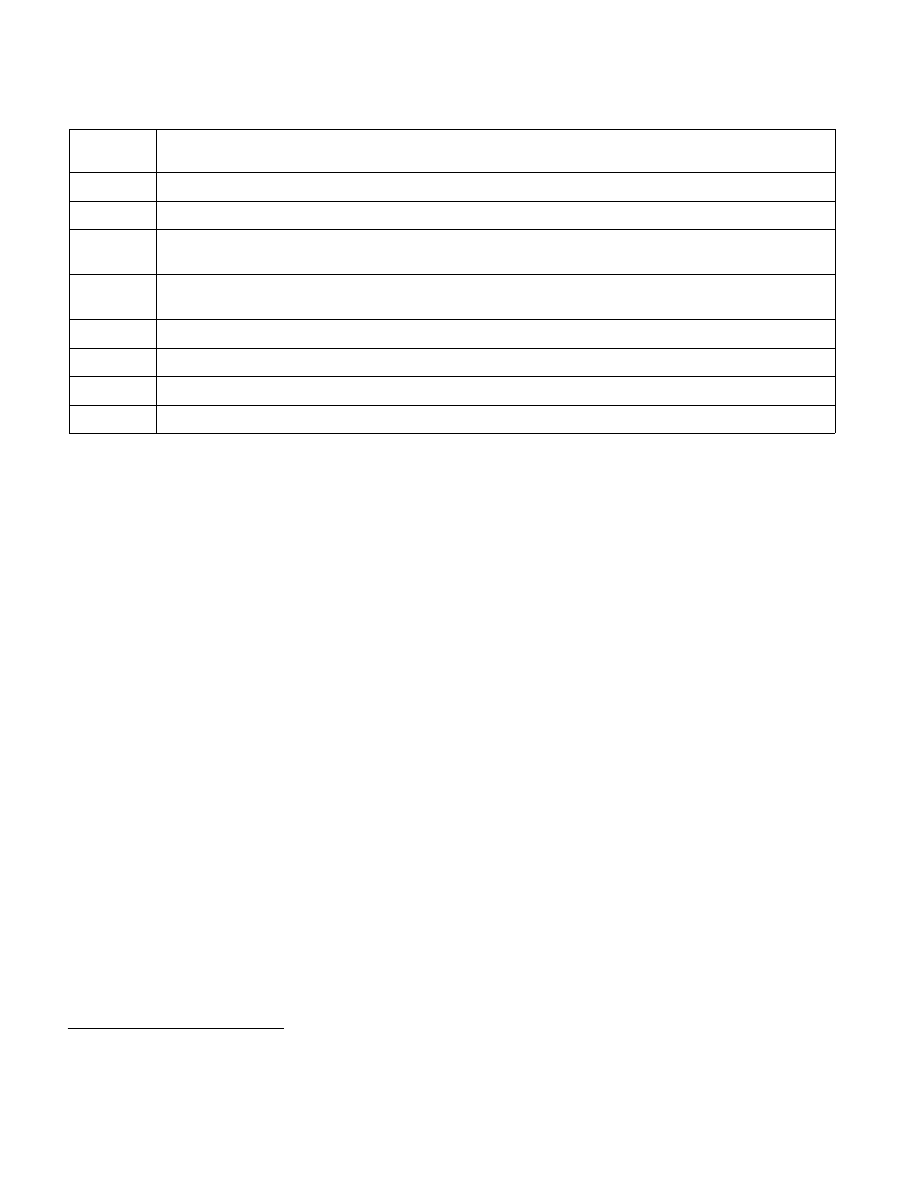
Table 4-8. Format of a PAE Page-Directory-Pointer-Table Entry (PDPTE)
Bit
Position(s)
Contents
0 (P)
Present; must be 1 to reference a page directory
2:1
Reserved (must be 0)
3 (PWT)
Page-level write-through; indirectly determines the memory type used to access the page directory referenced by
this entry (see Section 4.9)
4 (PCD)
Page-level cache disable; indirectly determines the memory type used to access the page directory referenced by
this entry (see Section 4.9)
8:5
Reserved (must be 0)
11:9
Ignored
(M–1):12
Physical address of 4-KByte aligned page directory referenced by this entry
1
63:M
Reserved (must be 0)
NOTES:
1. M is an abbreviation for MAXPHYADDR, which is at most 52; see Section 4.1.4.
1. With PAE paging, the processor does not use CR3 when translating a linear address (as it does in the other paging modes). It does
not access the PDPTEs in the page-directory-pointer table during linear-address translation.