Vol. 3A 10-11
ADVANCED PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (APIC)
•
By asserting the processor’s INIT# pin.
•
By sending the processor an INIT IPI (an IPI with the delivery mode set to INIT).
Upon receiving an INIT through either of these mechanisms, the processor responds by beginning the initialization
process of the processor core and the local APIC. The state of the local APIC following an INIT reset is the same as
it is after a power-up or hardware reset, except that the APIC ID and arbitration ID registers are not affected. This
state is also referred to at the “wait-for-SIPI” state (see also: Section 8.4.2, “MP Initialization Protocol Require-
ments and Restrictions”).
10.4.7.4 Local APIC State After It Receives an INIT-Deassert IPI
Only the Pentium and P6 family processors support the INIT-deassert IPI. An INIT-deassert IPI has no affect on the
state of the APIC, other than to reload the arbitration ID register with the value in the APIC ID register.
10.4.8
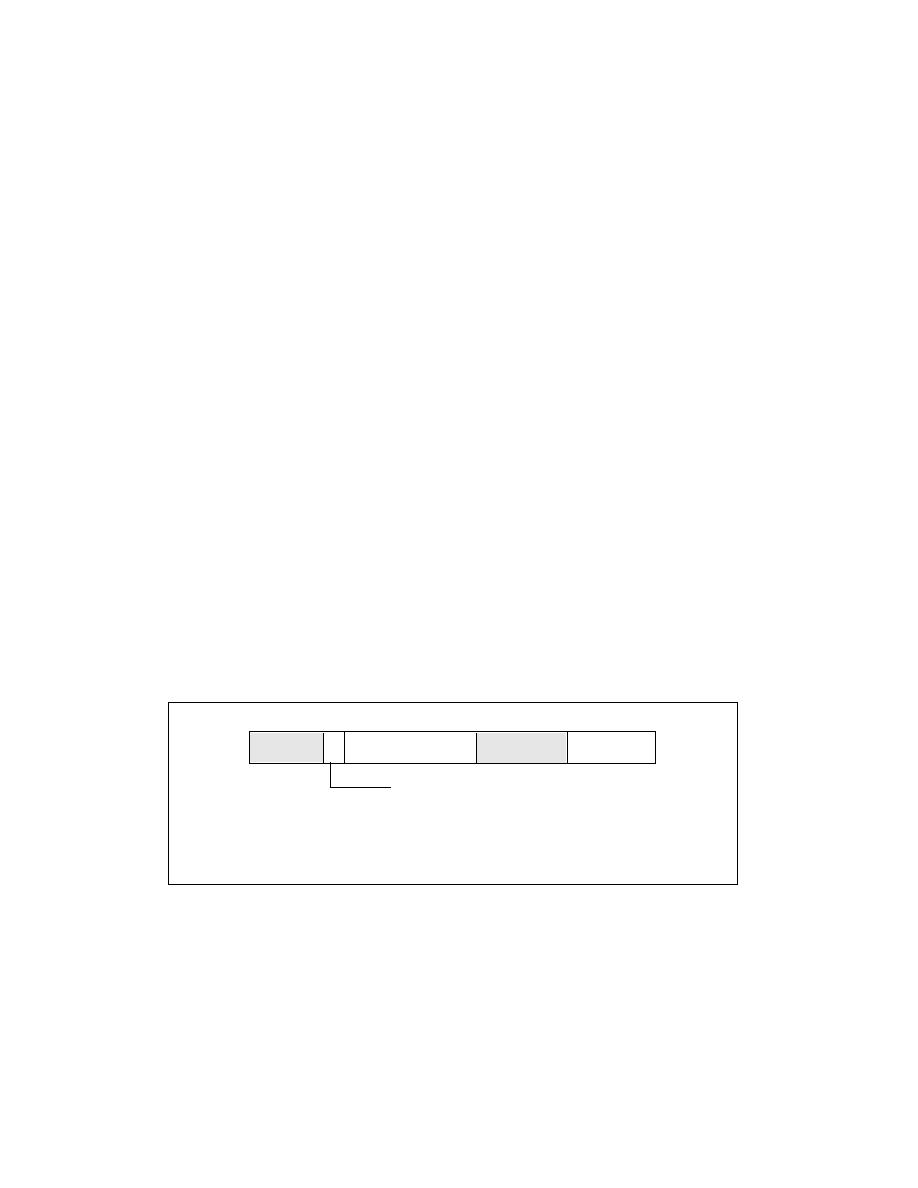
Local APIC Version Register
The local APIC contains a hardwired version register. Software can use this register to identify the APIC version
(see Figure 10-7). In addition, the register specifies the number of entries in the local vector table (LVT) for a
specific implementation.
The fields in the local APIC version register are as follows:
Version
The version numbers of the local APIC:
0XH
82489DX discrete APIC.
10H - 15H
Integrated APIC.
Other values reserved.
Max LVT Entry
Shows the number of LVT entries minus 1. For the Pentium 4 and Intel Xeon processors (which
have 6 LVT entries), the value returned in the Max LVT field is 5; for the P6 family processors
(which have 5 LVT entries), the value returned is 4; for the Pentium processor (which has 4 LVT
entries), the value returned is 3. For processors based on the Intel microarchitecture code
name Nehalem (which has 7 LVT entries) and onward, the value returned is 6.
Suppress EOI-broadcasts
Indicates whether software can inhibit the broadcast of EOI message by setting bit 12 of the
Spurious Interrupt Vector Register; see Section 10.8.5 and Section 10.9.
10.5
HANDLING LOCAL INTERRUPTS
The following sections describe facilities that are provided in the local APIC for handling local interrupts. These
include: the processor’s LINT0 and LINT1 pins, the APIC timer, the performance-monitoring counters, the thermal
sensor, and the internal APIC error detector. Local interrupt handling facilities include: the LVT, the error status
register (ESR), the divide configuration register (DCR), and the initial count and current count registers.
Figure 10-7. Local APIC Version Register
31
0
Reserved
7
8
23
15
Support for EOI-broadcast suppression
16
Reserved
25 24
Version
Max LVT Entry
Value after reset: 00BN 00VVH
V = Version, N = # of LVT entries minus 1,
Address: FEE0 0030H
B = 1 if EOI-broadcast suppression supported