6-2 Vol. 3A
INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING
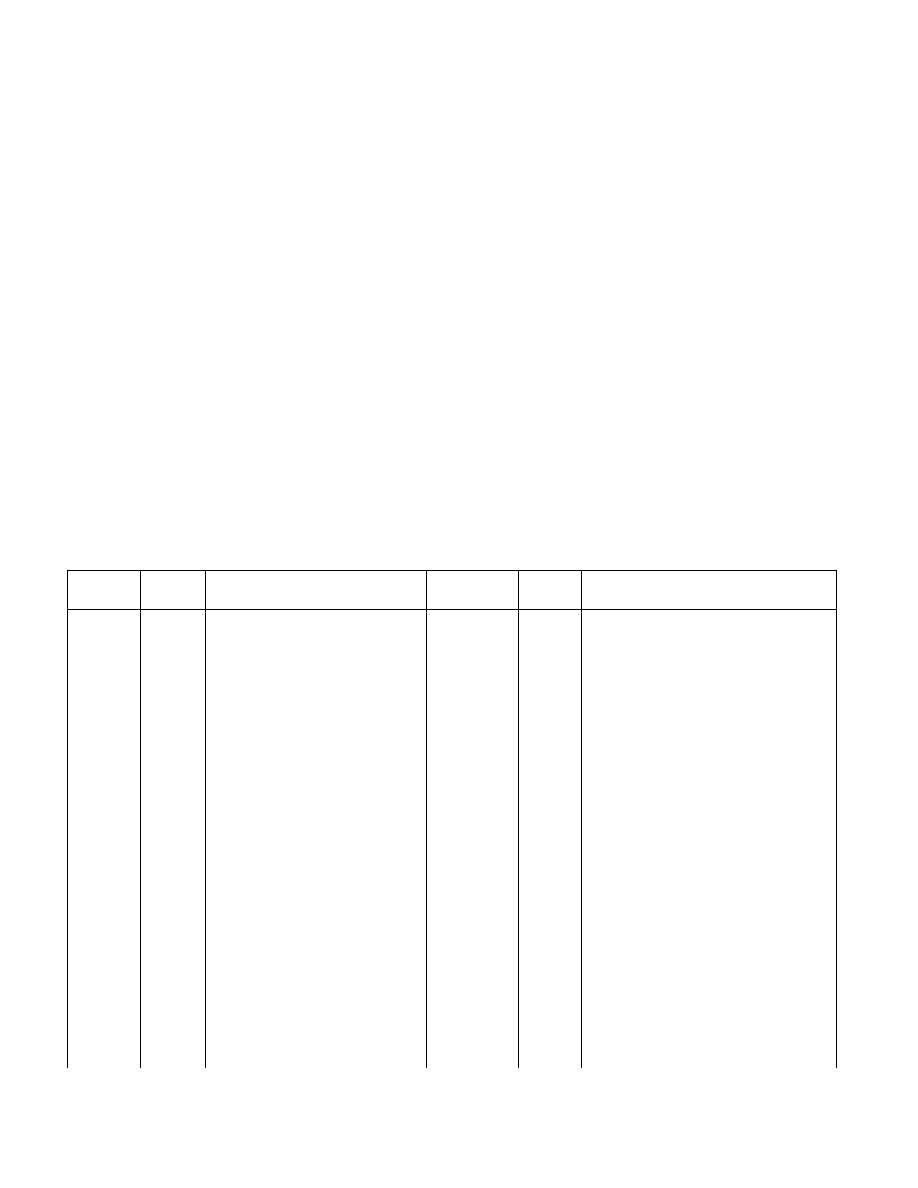
Table 6-1 shows vector number assignments for architecturally defined exceptions and for the NMI interrupt. This
table gives the exception type (see Section 6.5, ŌĆ£Exception ClassificationsŌĆØ) and indicates whether an error code is
saved on the stack for the exception. The source of each predefined exception and the NMI interrupt is also given.
6.3 SOURCES
OF
INTERRUPTS
The processor receives interrupts from two sources:
ŌĆó
External (hardware generated) interrupts.
ŌĆó
Software-generated interrupts.
6.3.1 External
Interrupts
External interrupts are received through pins on the processor or through the local APIC. The primary interrupt pins
on Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, P6 family, and Pentium processors are the LINT[1:0] pins, which are connected to the
local APIC (see Chapter 10, ŌĆ£Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC)ŌĆØ). When the local APIC is
enabled, the LINT[1:0] pins can be programmed through the APICŌĆÖs local vector table (LVT) to be associated with
any of the processorŌĆÖs exception or interrupt vectors.
When the local APIC is global/hardware disabled, these pins are configured as INTR and NMI pins, respectively.
Asserting the INTR pin signals the processor that an external interrupt has occurred. The processor reads from the
system bus the interrupt vector number provided by an external interrupt controller, such as an 8259A (see Section
6.2, ŌĆ£Exception and Interrupt VectorsŌĆØ). Asserting the NMI pin signals a non-maskable interrupt (NMI), which is
assigned to interrupt vector 2.
Table 6-1. Protected-Mode Exceptions and Interrupts
Vector
Mne-
monic
Description
Type
Error
Code
Source
0
#DE
Divide Error
Fault
No
DIV and IDIV instructions.
1
#DB
Debug Exception
Fault/ Trap
No
Instruction, data, and I/O breakpoints;
single-step; and others.
2
ŌĆö
NMI Interrupt
Interrupt
No
Nonmaskable external interrupt.
3
#BP
Breakpoint
Trap
No
INT 3 instruction.
4
#OF
Overflow
Trap
No
INTO instruction.
5
#BR
BOUND Range Exceeded
Fault
No
BOUND instruction.
6
#UD
Invalid Opcode (Undefined Opcode)
Fault
No
UD2 instruction or reserved opcode.
1
7
#NM
Device Not Available (No Math
Coprocessor)
Fault
No
Floating-point or WAIT/FWAIT instruction.
8
#DF
Double Fault
Abort
Yes
(zero)
Any instruction that can generate an
exception, an NMI, or an INTR.
9
Coprocessor Segment Overrun
(reserved)
Fault
No
Floating-point instruction.
2
10
#TS
Invalid TSS
Fault
Yes
Task switch or TSS access.
11
#NP
Segment Not Present
Fault
Yes
Loading segment registers or accessing
system segments.
12
#SS
Stack-Segment Fault
Fault
Yes
Stack operations and SS register loads.
13
#GP
General Protection
Fault
Yes
Any memory reference and other
protection checks.
14
#PF
Page Fault
Fault
Yes
Any memory reference.