36-36 Vol. 3C
INTEL® PROCESSOR TRACE
36.4.2 Packet
Definitions
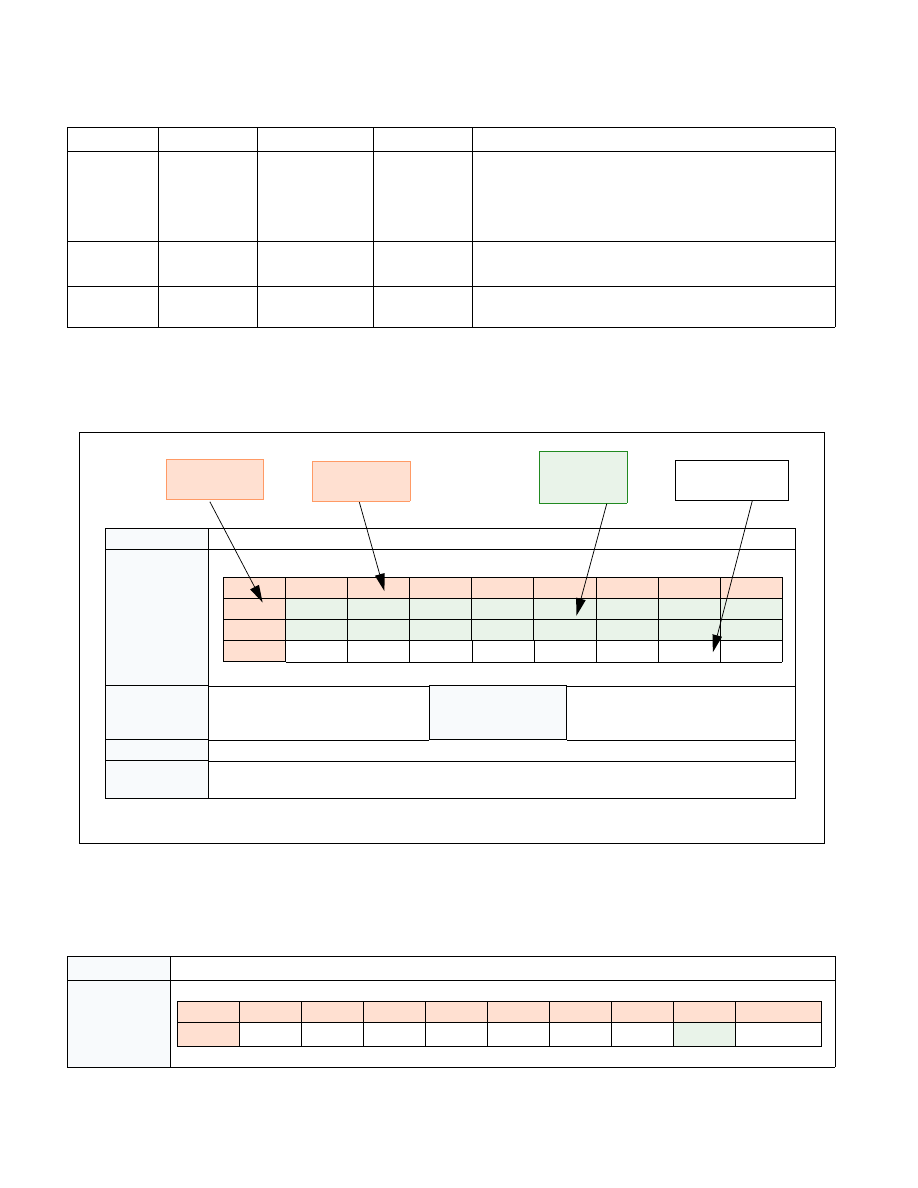
The following description of packet definitions are in tabular format. Figure 36-3 explains how to interpret them.
Packet bits listed as “RSVD” are not guaranteed to be 0.
36.4.2.1 Taken/Not-taken (TNT) Packet
Table 36-15. Compound Packet Event Summary
Event Type
Beginning
Middle
End
Comment
Unconditional
,
uncompresse
d control-flow
transfer
FUP or none
Any combination
of PIP, VMCS,
MODE.Exec, or
none
TIP or TIP.PGD
FUP only for asynchronous events. Order of middle packets
may vary.
PIP/VMCS/MODE only if the operation modifies the state
tracked by these respective packets
TSX Update
MODE.TSX, and
(FUP or none)
None
TIP, TIP.PGD, or
none
FUP
TIP/TIP.PGD only for TSX abort cases
Overflow
OVF
PSB, PSBEND, or
none
FUP or TIP.PGE FUP if overflow resolves while ContextEn=1, else TIP.PGE.
Figure 36-3. Interpreting Tabular Definition of Packet Format
Table 36-16. TNT Packet Definition
Name
Taken/Not-taken (TNT) Packet
Packet Format
Name
Packet name
Packet Format
Description of fields
Dependencies
Depends on packet generation con-
figuration enable controls or other
Generation Scenario
Which instructions, events, or other
scenarios can cause this packet to be
generated.
Description
Description of the packet, including the purpose it serves, meaning of the information or payload, etc
Application
How a decoder should apply this packet. It may bind to a specific instruction from the binary, or to
another packet in the stream, or have other implications on decode
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
Byte Number
Payload in White
Header bits
in Green
Bit Number
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
1
B
1
B
2
B
3
B
4
B
5
B
6
0
Short TNT