34-20 Vol. 3C
SYSTEM MANAGEMENT MODE
34.15.2.1 Architectural State Before a VM Exit
System-management interrupts (SMIs) that cause SMM VM exits always do so directly. They do not save state to
SMRAM as they do under the default treatment.
34.15.2.2 Updating the Current-VMCS and Executive-VMCS Pointers
SMM VM exits begin by performing the following steps:
1. The executive-VMCS pointer field in the SMM-transfer VMCS is loaded as follows:
— If the SMM VM exit commenced in VMX non-root operation, it receives the current-VMCS pointer.
— If the SMM VM exit commenced in VMX root operation, it receives the VMXON pointer.
2. The current-VMCS pointer is loaded with the value of the SMM-transfer VMCS pointer.
The last step ensures that the current VMCS is the SMM-transfer VMCS. VM-exit information is recorded in that
VMCS, and VM-entry control fields in that VMCS are updated. State is saved into the guest-state area of that VMCS.
The VM-exit controls and host-state area of that VMCS determine how the VM exit operates.
34.15.2.3 Recording VM-Exit Information
SMM VM exits differ from other VM exit with regard to the way they record VM-exit information. The differences
follow.
•
Exit reason.
— Bits 15:0 of this field contain the basic exit reason. The field is loaded with the reason for the SMM VM exit:
I/O SMI (an SMI arrived immediately after retirement of an I/O instruction), other SMI, or VMCALL. See
Appendix C, “VMX Basic Exit Reasons”.
— SMM VM exits are the only VM exits that may occur in VMX root operation. Because the SMM-transfer
monitor may need to know whether it was invoked from VMX root or VMX non-root operation, this
information is stored in bit 29 of the exit-reason field (see Table 24-14 in Section 24.9.1). The bit is set by
SMM VM exits from VMX root operation.
— If the SMM VM exit occurred in VMX non-root operation and an MTF VM exit was pending, bit 28 of the exit-
reason field is set; otherwise, it is cleared.
— Bits 27:16 and bits 31:30 are cleared.
•
Exit qualification. For an SMM VM exit due an SMI that arrives immediately after the retirement of an I/O
instruction, the exit qualification contains information about the I/O instruction that retired immediately before
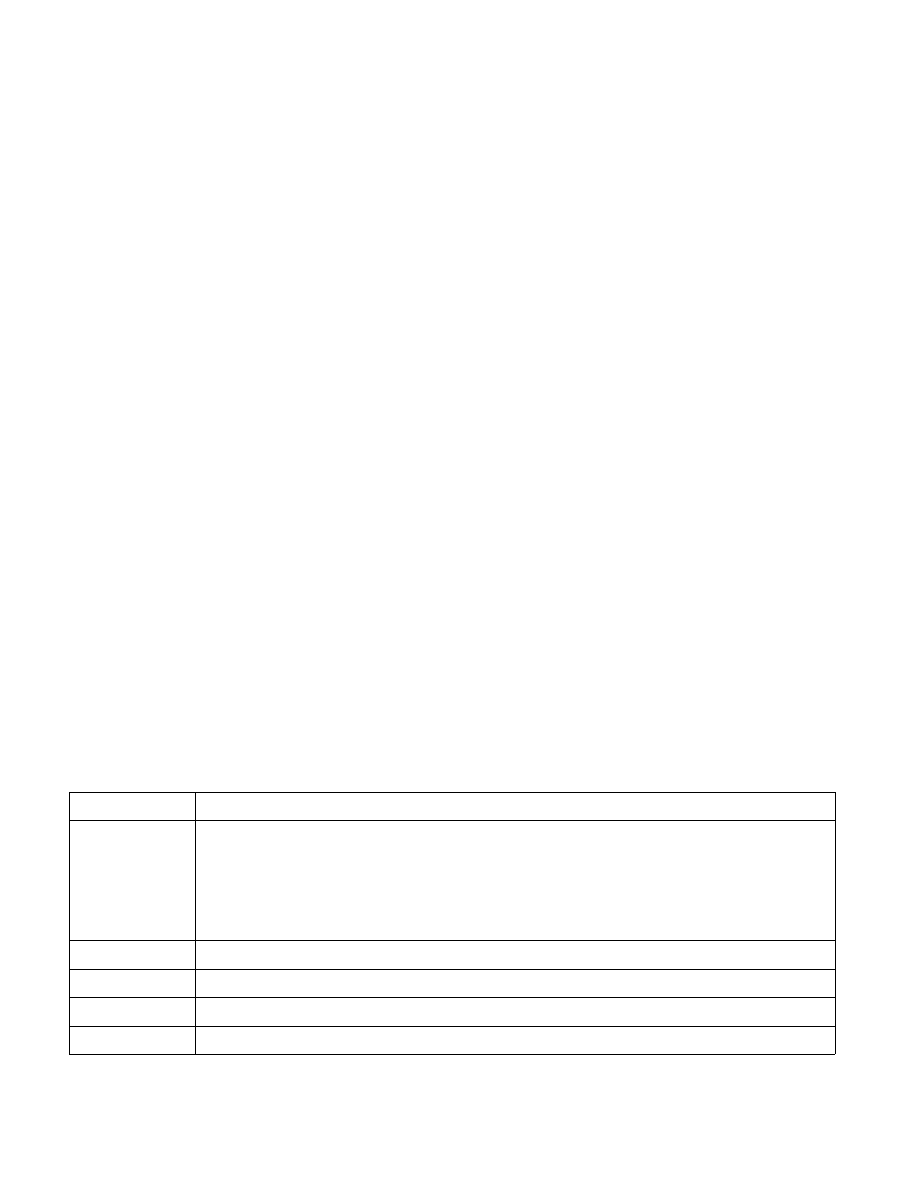
the SMI. It has the format given in Table 34-9.
Table 34-9. Exit Qualification for SMIs That Arrive Immediately After the Retirement of an I/O Instruction
Bit Position(s)
Contents
2:0
Size of access:
0 = 1-byte
1 = 2-byte
3 = 4-byte
Other values not used.
3
Direction of the attempted access (0 = OUT, 1 = IN)
4
String instruction (0 = not string; 1 = string)
5
REP prefixed (0 = not REP; 1 = REP)
6
Operand encoding (0 = DX, 1 = immediate)