25-16 Vol. 3C
VMX NON-ROOT OPERATION
•
If bit 7 of the entry is 1, or if the entry is an EPT PTE, the entry maps a page. If the processor uses such
an entry to translate a guest-physical address, and if an access to that address causes an EPT violation,
the EPT violation is convertible if and only if bit 63 of the entry is 0.
•
If bit 7 of the entry is 0 and the entry is not an EPT PTE, the entry references another EPT paging
structure. The processor does not use the value of bit 63 of the entry to determine whether any
subsequent EPT violation is convertible.
If an access to a guest-physical address causes an EPT violation, bit 63 of exactly one of the EPT paging-structure
entries used to translate that address is used to determine whether the EPT violation is convertible: either a entry
that is not present (if the guest-physical address does not translate to a physical address) or an entry that maps a
page (if it does).
A convertible EPT violation instead causes a virtualization exception if the following all hold:
•
CR0.PE = 1;
•
the logical processor is not in the process of delivering an event through the IDT; and
•
the 32 bits at offset 4 in the virtualization-exception information area are all 0.
Delivery of virtualization exceptions writes the value FFFFFFFFH to offset 4 in the virtualization-exception informa-
tion area (see Section 25.5.6.2). Thus, once a virtualization exception occurs, another can occur only if software
clears this field.
25.5.6.2 Virtualization-Exception Information
Virtualization exceptions save data into the virtualization-exception information area (see Section 24.6.18).
Table 25-1 enumerates the data saved and the format of the area.
25.5.6.3 Delivery of Virtualization Exceptions
After saving virtualization-exception information, the processor treats a virtualization exception as it does other
exceptions:
•
If bit 20 (#VE) is 1 in the exception bitmap in the VMCS, a virtualization exception causes a VM exit (see
below). If the bit is 0, the virtualization exception is delivered using gate descriptor 20 in the IDT.
•
Virtualization exceptions produce no error code. Delivery of a virtualization exception pushes no error code on
the stack.
•
With respect to double faults, virtualization exceptions have the same severity as page faults. If delivery of a
virtualization exception encounters a nested fault that is either contributory or a page fault, a double fault
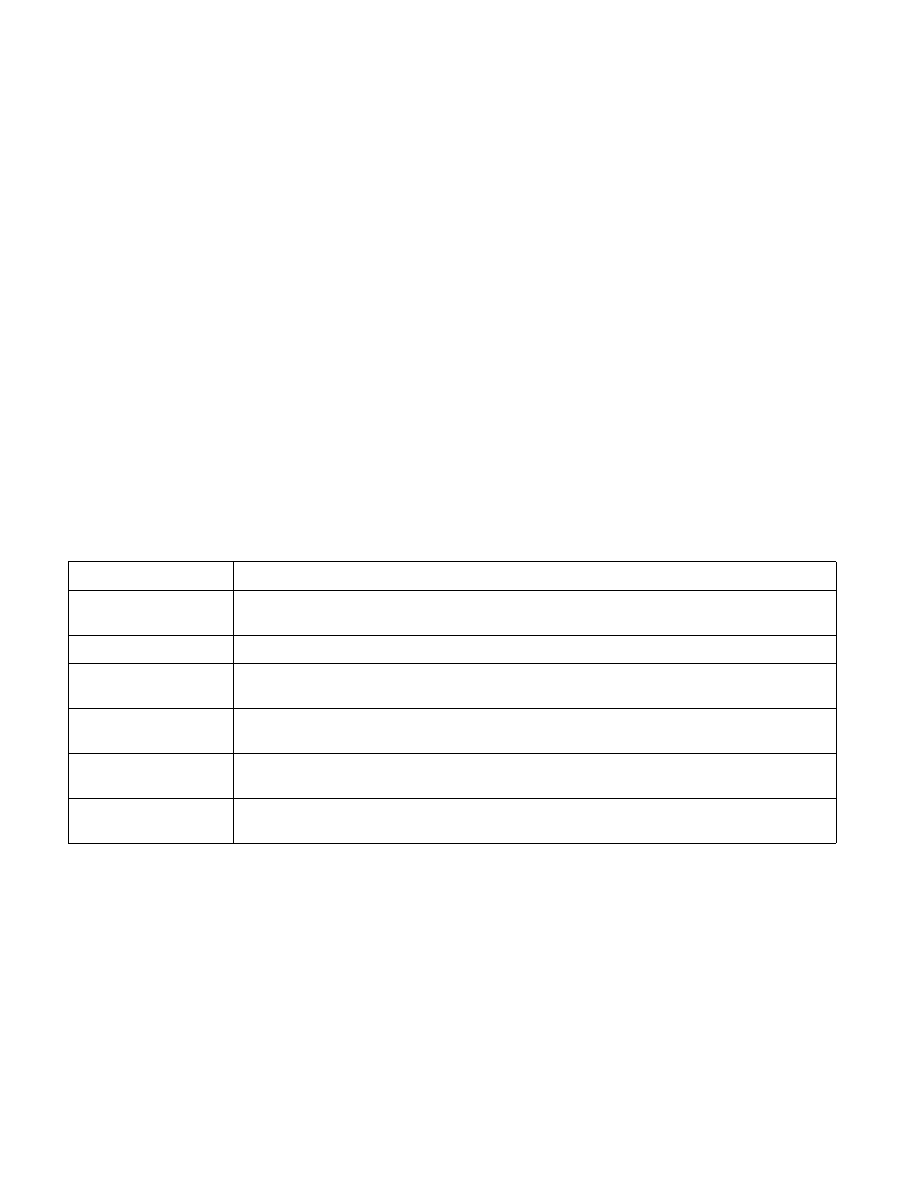
Table 25-1. Format of the Virtualization-Exception Information Area
Byte Offset
Contents
0
The 32-bit value that would have been saved into the VMCS as an exit reason had a VM exit occurred
instead of the virtualization exception. For EPT violations, this value is 48 (00000030H)
4
FFFFFFFFH
8
The 64-bit value that would have been saved into the VMCS as an exit qualification had a VM exit
occurred instead of the virtualization exception
16
The 64-bit value that would have been saved into the VMCS as a guest-linear address had a VM exit
occurred instead of the virtualization exception
24
The 64-bit value that would have been saved into the VMCS as a guest-physical address had a VM
exit occurred instead of the virtualization exception
32
The current 16-bit value of the EPTP index VM-execution control (see Section 24.6.18 and Section