Vol. 1 8-21
PROGRAMMING WITH THE X87 FPU
first be moved to the AX register in the integer unit. The FSTSW AX (store status word) instruction can be used for
this purpose. When these flags are in the AX register, the TEST instruction can be used to control conditional
branching as follows:
1. Check for an unordered result. Use the TEST instruction to compare the contents of the AX register with the
constant 0400H (see Table 8-8). This operation will clear the ZF flag in the EFLAGS register if the condition code
flags indicate an unordered result; otherwise, the ZF flag will be set. The JNZ instruction can then be used to
transfer control (if necessary) to a procedure for handling unordered operands.
2. Check ordered comparison result. Use the constants given in Table 8-8 in the TEST instruction to test for a less
than, equal to, or greater than result, then use the corresponding conditional branch instruction to transfer
program control to the appropriate procedure or section of code.
If a program or procedure has been thoroughly tested and it incorporates periodic checks for QNaN results, then it
is not necessary to check for the unordered result every time a comparison is made.
See Section 8.1.4, “Branching and Conditional Moves on Condition Codes,” for another technique for branching on
x87 FPU condition codes.
Some non-comparison x87 FPU instructions update the condition code flags in the x87 FPU status word. To ensure
that the status word is not altered inadvertently, store it immediately following a comparison operation.
8.3.7 Trigonometric
Instructions
The following instructions perform four common trigonometric functions:
FSIN
Sine
FCOS
Cosine
FSINCOS
Sine and cosine
FPTAN
Tangent
FPATAN
Arctangent
These instructions operate on the top one or two registers of the x87 FPU register stack and they return their
results to the stack. The source operands for the FSIN, FCOS, FSINCOS, and FPTAN instructions must be given in
radians; the source operand for the FPATAN instruction is given in rectangular coordinate units.
The FSINCOS instruction returns both the sine and the cosine of a source operand value. It operates faster than
executing the FSIN and FCOS instructions in succession.
The FPATAN instruction computes the arctangent of ST(1) divided by ST(0), returning a result in radians. It is
useful for converting rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates.
See Section 8.3.8, “Approximation of Pi” and Section 8.3.10, “Transcendental Instruction Accuracy” for information
regarding the accuracy of these instructions.
8.3.8
Approximation of Pi
When the argument (source operand) of a trigonometric function is within the domain of the function, the argu-
ment is automatically reduced by the appropriate multiple of 2π through the same reduction mechanism used by
the FPREM and FPREM1 instructions. The internal value of π (3.1415926…) that the x87 FPU uses for argument
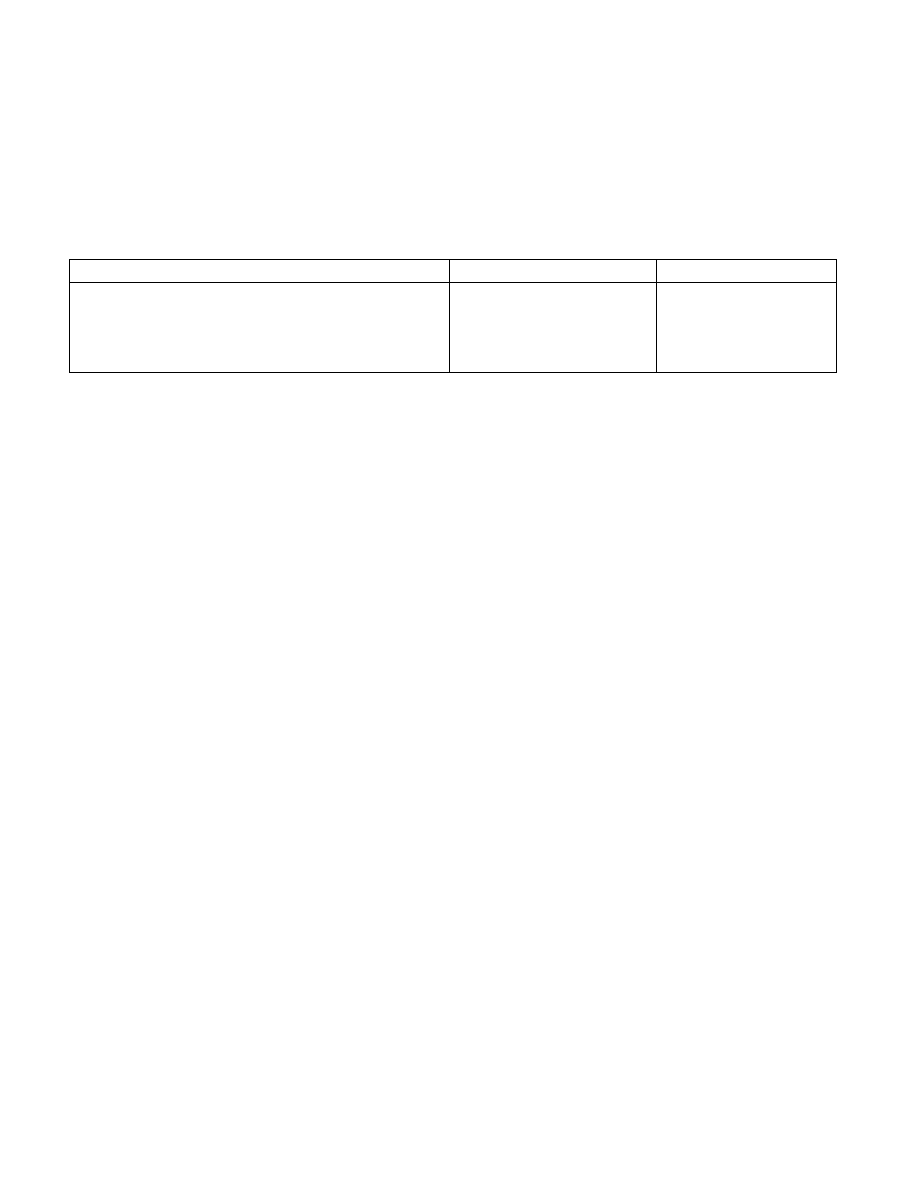
Table 8-8. TEST Instruction Constants for Conditional Branching
Order
Constant
Branch
ST(0) > Source Operand
4500H
JZ
ST(0) < Source Operand
0100H
JNZ
ST(0) = Source Operand
4000H
JNZ
Unordered
0400H
JNZ