15-18 Vol. 3B
MACHINE-CHECK ARCHITECTURE
•
UCR errors will overwrite corrected errors.
•
Uncorrected (PCC=1) errors overwrite UCR (PCC=0) errors.
•
UCR errors are not written over previous UCR errors.
•
Corrected errors do not write over previous UCR errors.
Regardless of whether the 1st error is retained or the 2nd error is overwritten over the 1st error, the OVER flag in
the IA32_MCi_STATUS register will be set to indicate an overflow condition. As the S flag and AR flag in the
IA32_MCi_STATUS register are defined to be sticky flags, a second event cannot clear these 2 flags once set,
however the MC bank information may be filled in for the 2nd error. The table below shows the overwrite rules and
how to treat a second error if the first event is already logged in a MC bank along with the resulting bit setting of
the UC, PCC, and AR flags in the IA32_MCi_STATUS register. As UCNA and SRA0 errors do not require recovery
action from system software to continue program execution, a system reset by system software is not required
unless the AR flag or PCC flag is set for the UCR overflow case (OVER=1, VAL=1, UC=1, PCC=0).
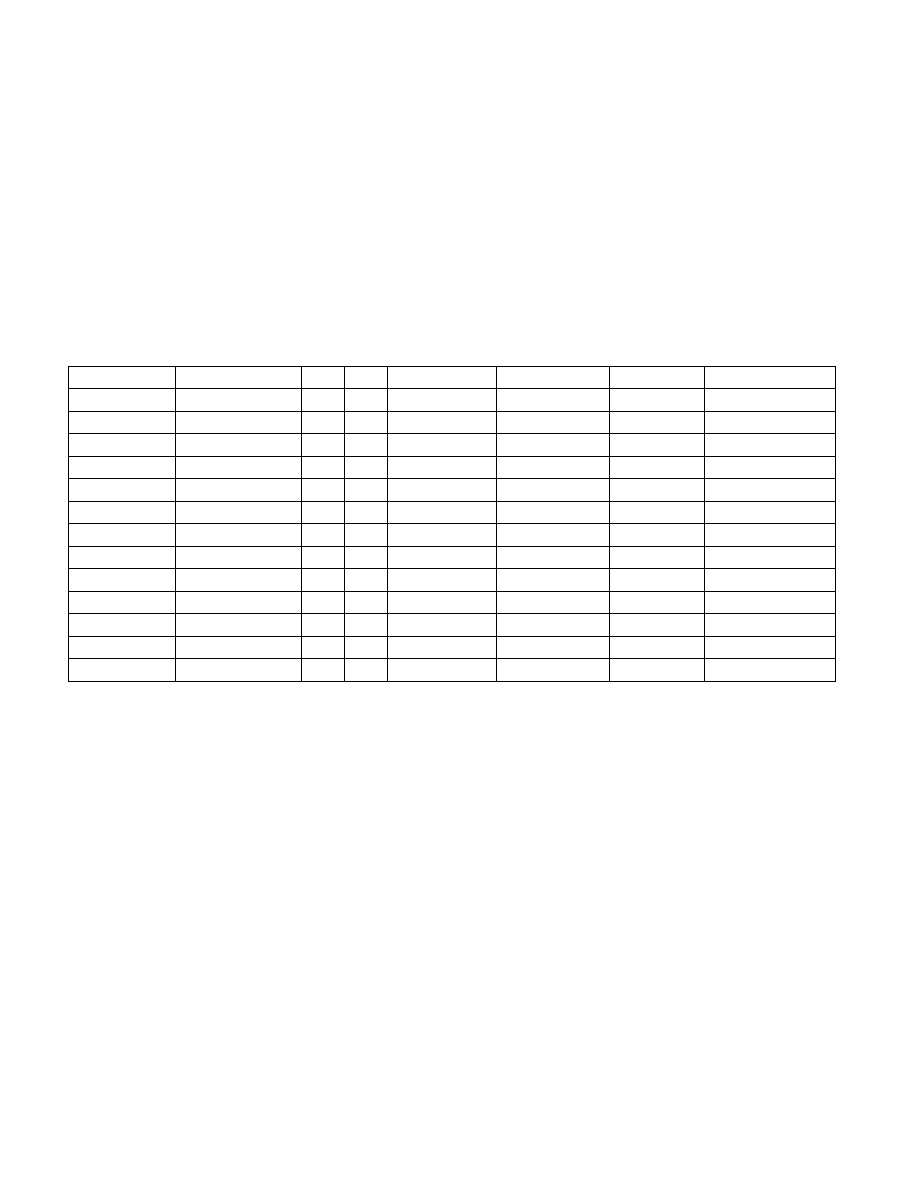
Table 15-7 lists overwrite rules for uncorrected errors, corrected errors, and uncorrected recoverable errors.
15.7 MACHINE-CHECK
AVAILABILITY
The machine-check architecture and machine-check exception (#MC) are model-specific features. Software can
execute the CPUID instruction to determine whether a processor implements these features. Following the execu-
tion of the CPUID instruction, the settings of the MCA flag (bit 14) and MCE flag (bit 7) in EDX indicate whether the
processor implements the machine-check architecture and machine-check exception.
15.8 MACHINE-CHECK
INITIALIZATION
To use the processors machine-check architecture, software must initialize the processor to activate the machine-
check exception and the error-reporting mechanism.
Example 15-1 gives pseudocode for performing this initialization. This pseudocode checks for the existence of the
machine-check architecture and exception; it then enables machine-check exception and the error-reporting
register banks. The pseudocode shown is compatible with the Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, Intel Atom, P6 family, and
Pentium processors.
Following power up or power cycling, IA32_MCi_STATUS registers are not guaranteed to have valid data until after
they are initially cleared to zero by software (as shown in the initialization pseudocode in Example 15-1). In addi-
tion, when using P6 family processors, software must set MCi_STATUS registers to zero when doing a soft-reset.
Table 15-7. Overwrite Rules for UC, CE, and UCR Errors
First Event
Second Event
UC
PCC
S
AR
MCA Bank
Reset System
CE
UCR
1
0
0 if UCNA, else 1 1 if SRAR, else 0
second
yes, if AR=1
UCR
CE
1
0
0 if UCNA, else 1 1 if SRAR, else 0
first
yes, if AR=1
UCNA
UCNA
1
0
0
0
first
no
UCNA
SRAO
1
0
1
0
first
no
UCNA
SRAR
1
0
1
1
first
yes
SRAO
UCNA
1
0
1
0
first
no
SRAO
SRAO
1
0
1
0
first
no
SRAO
SRAR
1
0
1
1
first
yes
SRAR
UCNA
1
0
1
1
first
yes
SRAR
SRAO
1
0
1
1
first
yes
SRAR
SRAR
1
0
1
1
first
yes
UCR
UC
1
1
undefined
undefined
second
yes
UC
UCR
1
1
undefined
undefined
first
yes