Vol. 3D 39-1
ENCLAVE OPERATION
CHAPTER 39
ENCLAVE OPERATION
The following aspects of enclave operation are described in this chapter:
•
Enclave creation: Includes loading code and data from outside of enclave into the EPC and establishing the
enclave entity.
•
Adding pages and measuring the enclave.
•
Initialization of an enclave: Finalizes the cryptographic log and establishes the enclave identity and sealing
identity.
•
Enclave entry and exiting including:
— Controlled entry and exit.
— Asynchronous Enclave Exit (AEX) and resuming execution after an AEX.
39.1
CONSTRUCTING AN ENCLAVE
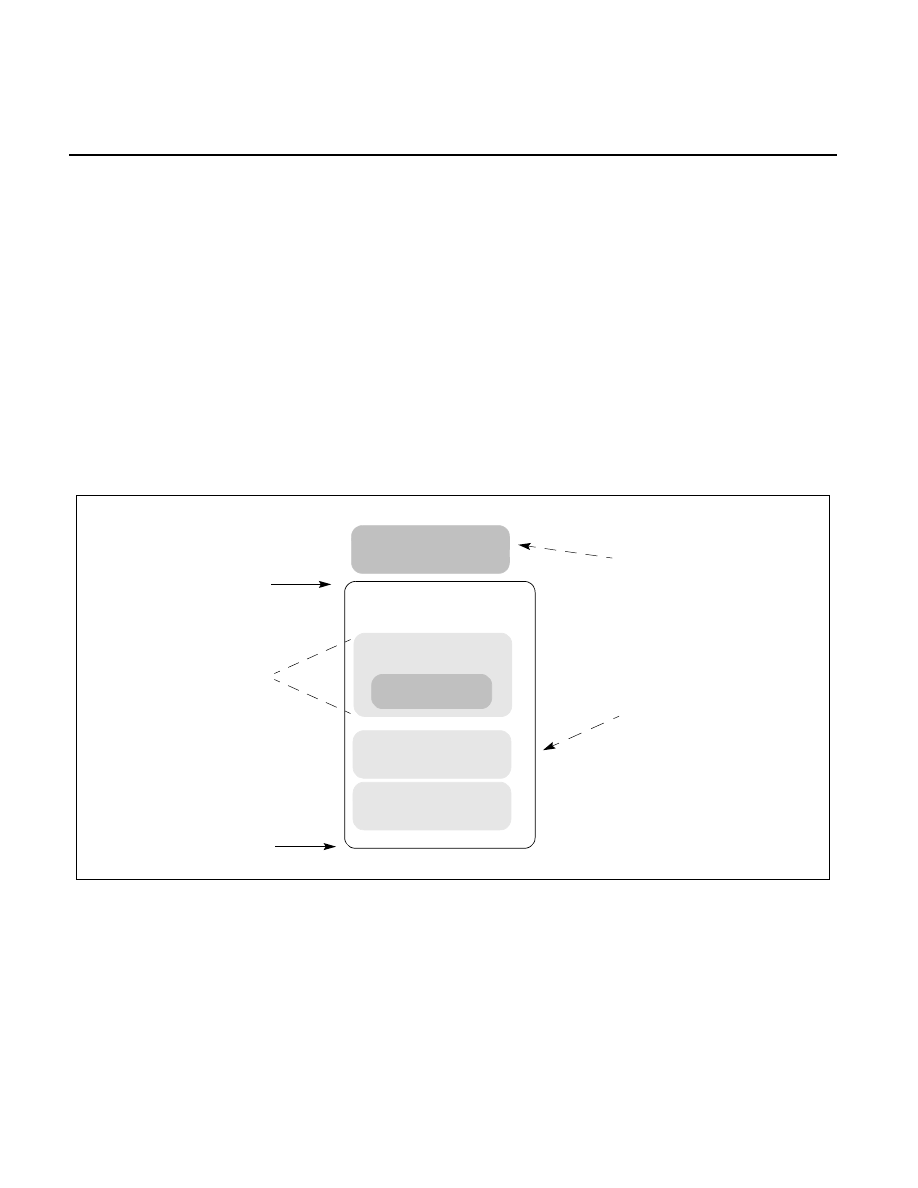
Figure 39-1 illustrates a typical Enclave memory layout.
The enclave creation, commitment of memory resources, and finalizing the enclave’s identity with measurement
comprises multiple phases. This process can be illustrated by the following exemplary steps:
1. The application hands over the enclave content along with additional information required by the enclave
creation API to the enclave creation service running at privilege level 0.
2. The enclave creation service running at privilege level 0 uses the ECREATE leaf function to set up the initial
environment, specifying base address and size of the enclave. This address range, the ELRANGE, is part of the
application's address space. This reserves the memory range. The enclave will now reside in this address
Figure 39-1. Enclave Memory Layout
Thread Data
Global Data
Code
Enclave Memory
SECS
TCS
Base + Size
Base
Replicated once
per thread
Enclave {Base, Size}
Application Context
OS Context