Vol. 3A 5-19
PROTECTION
The parameter count field in a call gate specifies the number of data items (up to 31) that the processor should
copy from the calling procedure’s stack to the stack of the called procedure. If more than 31 data items need to be
passed to the called procedure, one of the parameters can be a pointer to a data structure, or the saved contents
of the SS and ESP registers may be used to access parameters in the old stack space. The size of the data items
passed to the called procedure depends on the call gate size, as described in Section 5.8.3, “Call Gates.”
5.8.5.1
Stack Switching in 64-bit Mode
Although protection-check rules for call gates are unchanged from 32-bit mode, stack-switch changes in 64-bit
mode are different.
When stacks are switched as part of a 64-bit mode privilege-level change through a call gate, a new SS (stack
segment) descriptor is not loaded; 64-bit mode only loads an inner-level RSP from the TSS. The new SS is forced
to NULL and the SS selector’s RPL field is forced to the new CPL. The new SS is set to NULL in order to handle
nested far transfers (far CALL, INTn, interrupts and exceptions). The old SS and RSP are saved on the new stack.
On a subsequent far RET, the old SS is popped from the stack and loaded into the SS register. See Table 5-2.
In 64-bit mode, stack operations resulting from a privilege-level-changing far call or far return are eight-bytes wide
and change the RSP by eight. The mode does not support the automatic parameter-copy feature found in 32-bit
mode. The call-gate count field is ignored. Software can access the old stack, if necessary, by referencing the old
stack-segment selector and stack pointer saved on the new process stack.
In 64-bit mode, far RET is allowed to load a NULL SS under certain conditions. If the target mode is 64-bit mode
and the target CPL ≠
3, IRET allows SS to be loaded with a NULL selector. If the called procedure itself is inter-
rupted, the NULL SS is pushed on the stack frame. On the subsequent far RET, the NULL SS on the stack acts as a
flag to tell the processor not to load a new SS descriptor.
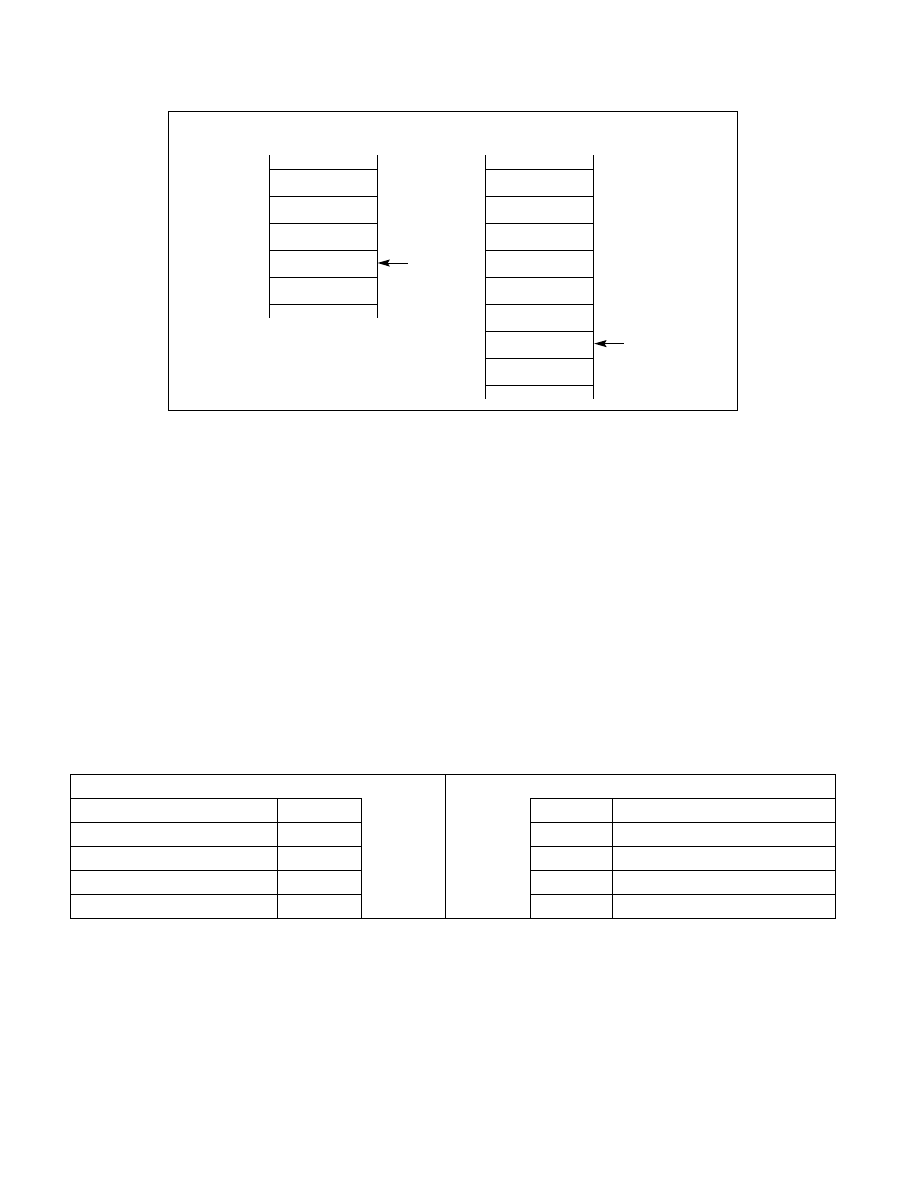
Figure 5-13. Stack Switching During an Interprivilege-Level Call
Table 5-2. 64-Bit-Mode Stack Layout After Far CALL with CPL Change
32-bit Mode
IA-32e mode
Old SS Selector
+12
+24
Old SS Selector
Old ESP
+8
+16
Old RSP
CS Selector
+4
+8
Old CS Selector
EIP
0
ESP
RSP
0
RIP
< 4 Bytes >
< 8 Bytes >
Parameter 1
Parameter 2
Parameter 3
Calling SS
Calling ESP
Parameter 1
Parameter 2
Parameter 3
Calling CS
Calling EIP
Called Procedure’s Stack
ESP
ESP
Calling Procedure’s Stack