5-14 Vol. 3A
PROTECTION
selected procedure through the gate. The P flag indicates whether the call-gate descriptor is valid. (The presence
of the code segment to which the gate points is indicated by the P flag in the code segment’s descriptor.) The
parameter count field indicates the number of parameters to copy from the calling procedures stack to the new
stack if a stack switch occurs (see Section 5.8.5, “Stack Switching”). The parameter count specifies the number of
words for 16-bit call gates and doublewords for 32-bit call gates.
Note that the P flag in a gate descriptor is normally always set to 1. If it is set to 0, a not present (#NP) exception
is generated when a program attempts to access the descriptor. The operating system can use the P flag for special
purposes. For example, it could be used to track the number of times the gate is used. Here, the P flag is initially
set to 0 causing a trap to the not-present exception handler. The exception handler then increments a counter and
sets the P flag to 1, so that on returning from the handler, the gate descriptor will be valid.
5.8.3.1
IA-32e Mode Call Gates
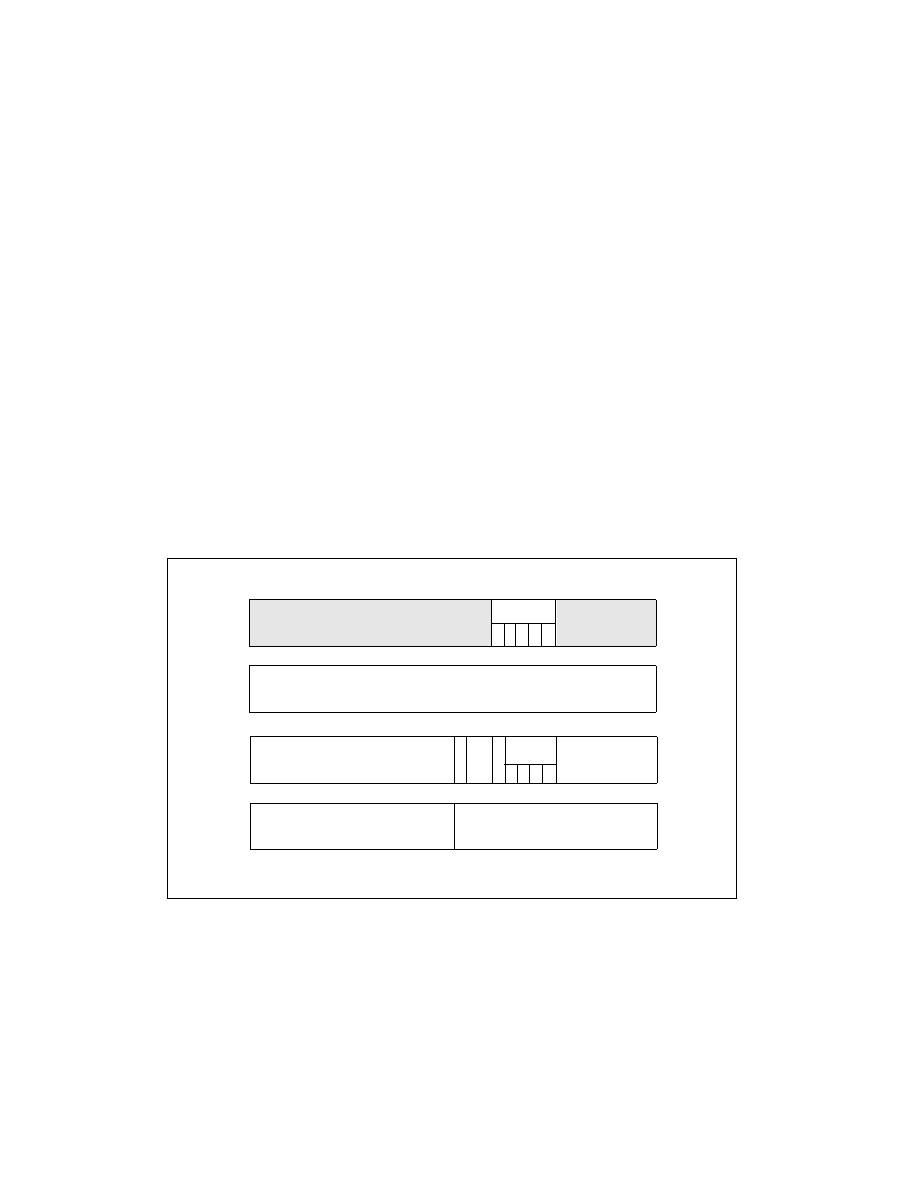
Call-gate descriptors in 32-bit mode provide a 32-bit offset for the instruction pointer (EIP); 64-bit extensions
double the size of 32-bit mode call gates in order to store 64-bit instruction pointers (RIP). See Figure 5-9:
•
The first eight bytes (bytes 7:0) of a 64-bit mode call gate are similar but not identical to legacy 32-bit mode
call gates. The parameter-copy-count field has been removed.
•
Bytes 11:8 hold the upper 32 bits of the target-segment offset in canonical form. A general-protection
exception (#GP) is generated if software attempts to use a call gate with a target offset that is not in canonical
form.
•
16-byte descriptors may reside in the same descriptor table with 16-bit and 32-bit descriptors. A type field,
used for consistency checking, is defined in bits 12:8 of the 64-bit descriptor’s highest dword (cleared to zero).
A general-protection exception (#GP) results if an attempt is made to access the upper half of a 64-bit mode
descriptor as a 32-bit mode descriptor.
•
Target code segments referenced by a 64-bit call gate must be 64-bit code segments (CS.L = 1, CS.D = 0). If
not, the reference generates a general-protection exception, #GP (CS selector).
•
Only 64-bit mode call gates can be referenced in IA-32e mode (64-bit mode and compatibility mode). The
legacy 32-bit mode call gate type (0CH) is redefined in IA-32e mode as a 64-bit call-gate type; no 32-bit call-
gate type exists in IA-32e mode.
Figure 5-9. Call-Gate Descriptor in IA-32e Mode
31
8 7
0
P
Offset in Segment 31:16
D
P
L
Type
0
4
31
16 15
0
Segment Selector
Offset in Segment 15:00
0
.
0
0
1
1
P
DPL
Gate Valid
Descriptor Privilege Level
31
0
0
12
31
0
Offset in Segment 63:31
8
0
0
0
0
0
13 12 11 10 9 8 7
16 15 14 13 12 11
Reserved
Reserved
Type