Vol. 2A 2-35
INSTRUCTION FORMAT
Any VEX-encoded GPR instruction with a 66H, F2H, or F3H prefix preceding VEX will #UD.
Any VEX-encoded GPR instruction with a REX prefix proceeding VEX will #UD.
VEX-encoded GPR instructions are not supported in real and virtual 8086 modes.
2.5.1
Exception Conditions for VEX-Encoded GPR Instructions
The exception conditions applicable to VEX-encoded GPR instruction differs from those of legacy GPR instructions.
Table 2-28 lists VEX-encoded GPR instructions. The exception conditions for VEX-encoded GRP instructions are
found in Table 2-29 for those instructions which have a default operand size of 32 bits and 16-bit operand size is
not encodable.
(*) - Additional exception restrictions are present - see the Instruction description for details.
2.6 INTEL®
AVX-512
ENCODING
The majority of the Intel AVX-512 family of instructions (operating on 512/256/128-bit vector register operands)
are encoded using a new prefix (called EVEX). Opmask instructions (operating on opmask register operands) are
encoded using the VEX prefix. The EVEX prefix has some parts resembling the instruction encoding scheme using
the VEX prefix, and many other capabilities not available with the VEX prefix.
The significant feature differences between EVEX and VEX are summarized below.
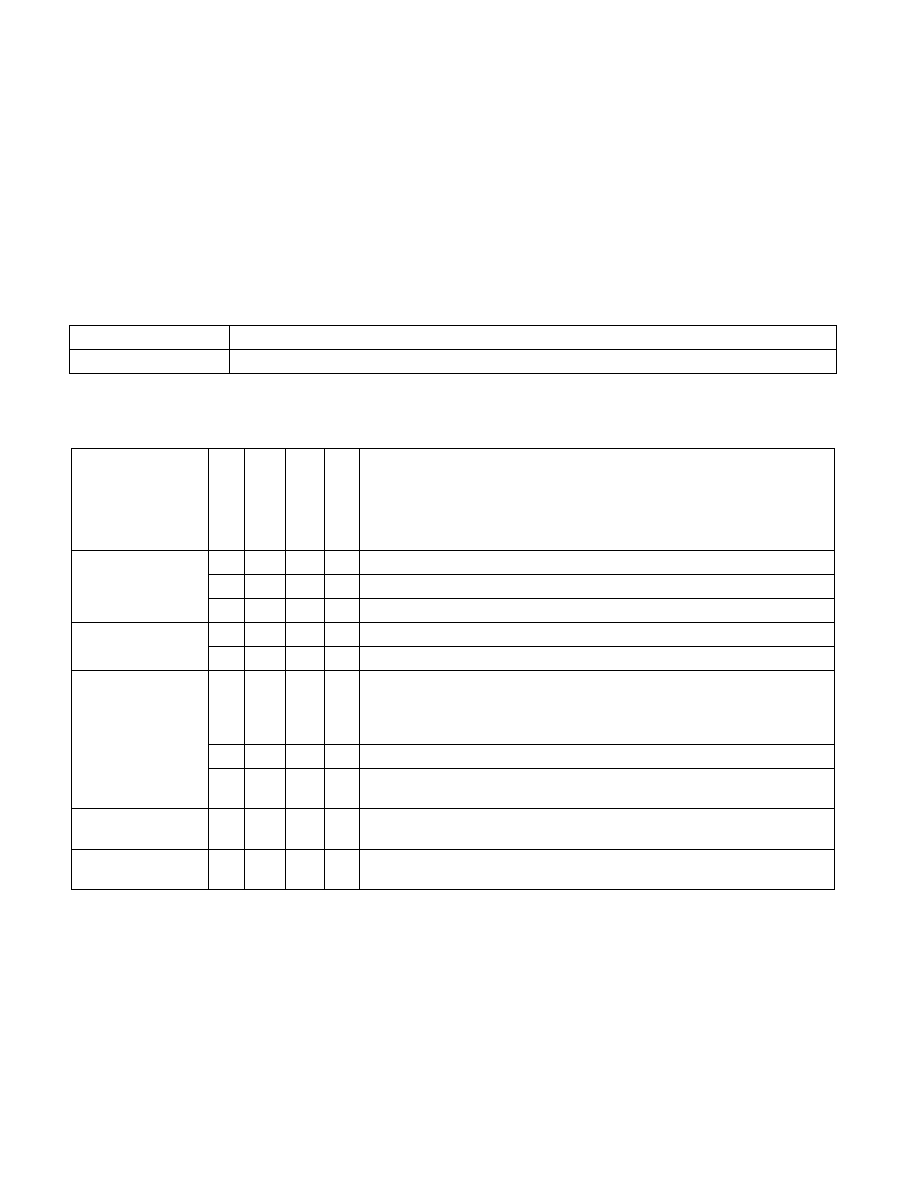
Table 2-28. VEX-Encoded GPR Instructions
Exception Class
Instruction
See Table 2-29
ANDN, BLSI, BLSMSK, BLSR, BZHI, MULX, PDEP, PEXT, RORX, SARX, SHLX, SHRX
Table 2-29. Exception Definition (VEX-Encoded GPR Instructions)
Exception
Re
al
Vi
rtual-8086
Pr
ot
ec
ted and
Co
mp
at
ib
ilit
y
64-b
it
Cause of Exception
Invalid Opcode, #UD
X
X
X
X
If BMI1/BMI2 CPUID feature flag is ‘0’.
X
X
If a VEX prefix is present.
X
X
If any REX, F2, F3, or 66 prefixes precede a VEX prefix.
Stack, SS(0)
X
X
X
For an illegal address in the SS segment.
X
If a memory address referencing the SS segment is in a non-canonical form.
General Protection,
#GP(0)
X
For an illegal memory operand effective address in the CS, DS, ES, FS or GS seg-
ments.
If the DS, ES, FS, or GS register is used to access memory and it contains a null
segment selector.
X
If the memory address is in a non-canonical form.
X
X
If any part of the operand lies outside the effective address space from 0 to
FFFFH.
Page Fault #PF(fault-
code)
X
X
X
For a page fault.
Alignment Check
#AC(0)
X
X
X
If alignment checking is enabled and an unaligned memory reference is made
while the current privilege level is 3.