4-10 Vol. 1
DATA TYPES
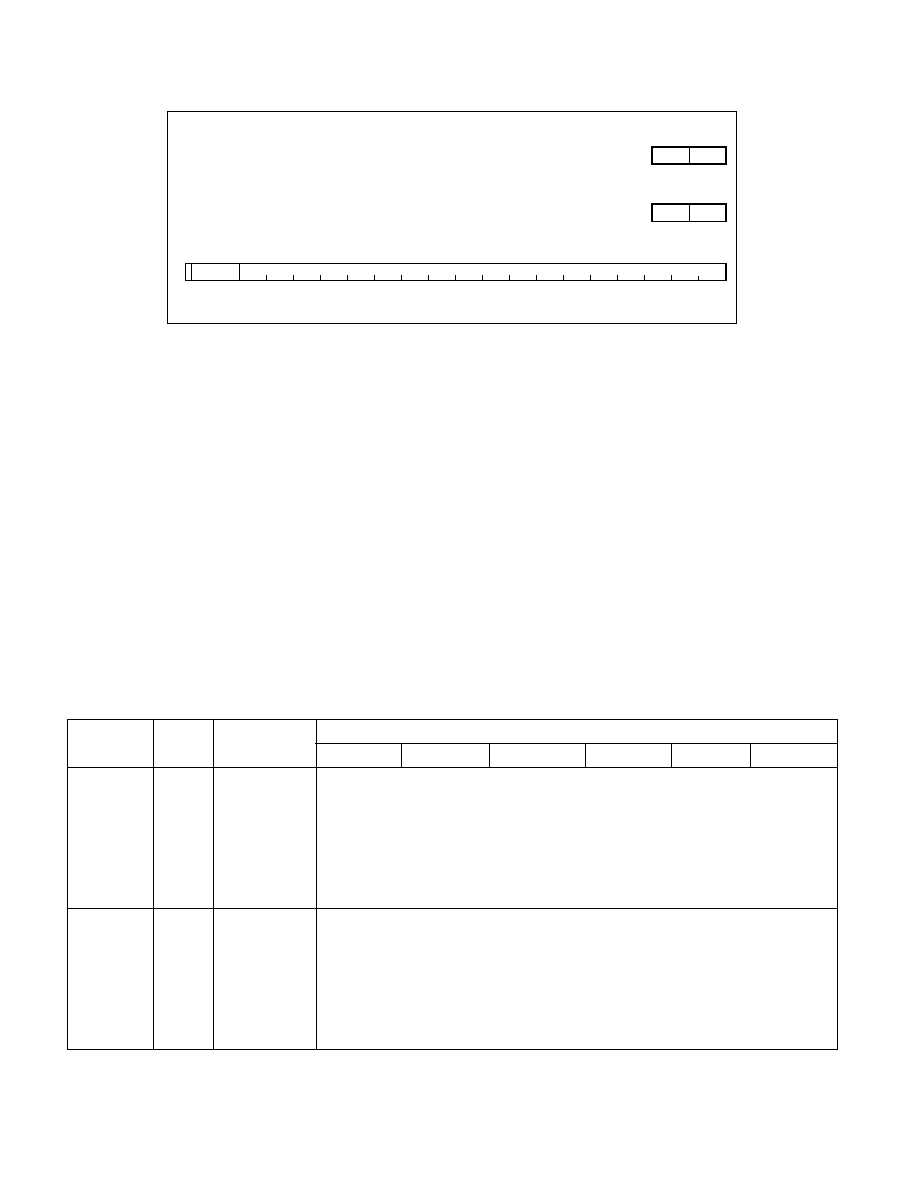
When operating on BCD integers in general-purpose registers, the BCD values can be unpacked (one BCD digit per
byte) or packed (two BCD digits per byte). The value of an unpacked BCD integer is the binary value of the low half-
byte (bits 0 through 3). The high half-byte (bits 4 through 7) can be any value during addition and subtraction, but
must be zero during multiplication and division. Packed BCD integers allow two BCD digits to be contained in one
byte. Here, the digit in the high half-byte is more significant than the digit in the low half-byte.
When operating on BCD integers in x87 FPU data registers, BCD values are packed in an 80-bit format and referred
to as decimal integers. In this format, the first 9 bytes hold 18 BCD digits, 2 digits per byte. The least-significant
digit is contained in the lower half-byte of byte 0 and the most-significant digit is contained in the upper half-byte
of byte 9. The most significant bit of byte 10 contains the sign bit (0 = positive and 1 = negative; bits 0 through 6
of byte 10 are don’t care bits). Negative decimal integers are not stored in two's complement form; they are distin-
guished from positive decimal integers only by the sign bit. The range of decimal integers that can be encoded in
this format is
–
10
18
+
1
to 10
18
–
1.
The decimal integer format exists in memory only. When a decimal integer is loaded in an x87 FPU data register, it
is automatically converted to the double-extended-precision floating-point format. All decimal integers are exactly
representable in double extended-precision format.
Table 4-4 gives the possible encodings of value in the decimal integer data type.
Figure 4-9. BCD Data Types
Table 4-4. Packed Decimal Integer Encodings
Magnitude
Class
Sign
digit
digit
digit
digit
...
digit
Positive
Largest
0
0000000
1001
1001
1001
1001
...
1001
.
.
.
.
.
.
Smallest
0
0000000
0000
0000
0000
0000
...
0001
Zero
0
0000000
0000
0000
0000
0000
...
0000
Negative
Zero
1
0000000
0000
0000
0000
0000
...
0000
Smallest
1
0000000
0000
0000
0000
0000
...
0001
.
.
.
.
.
.
Largest
1
0000000
1001
1001
1001
1001
...
1001
Packed BCD Integers
BCD
BCD
0
BCD Integers
7
BCD
X
3
4
0
80-Bit Packed BCD Decimal Integers
79
D0
4 Bits = 1 BCD Digit
Sign
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
D17
78
72 71
X
0
7
3
4