Vol. 1 2-17
INTEL
®
64 AND IA-32 ARCHITECTURES
2.2.8 Intel
®
Hyper-Threading Technology
Intel Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel HT Technology) was developed to improve the performance of IA-32
processors when executing multi-threaded operating system and application code or single-threaded applications
under multi-tasking environments. The technology enables a single physical processor to execute two or more
separate code streams (threads) concurrently using shared execution resources.
Intel HT Technology is one form of hardware multi-threading capability in IA-32 processor families. It differs from
multi-processor capability using separate physically distinct packages with each physical processor package mated
with a physical socket. Intel HT Technology provides hardware multi-threading capability with a single physical
package by using shared execution resources in a processor core.
Architecturally, an IA-32 processor that supports Intel HT Technology consists of two or more logical processors,
each of which has its own IA-32 architectural state. Each logical processor consists of a full set of IA-32 data regis-
ters, segment registers, control registers, debug registers, and most of the MSRs. Each also has its own advanced
programmable interrupt controller (APIC).
Figure 2-5 shows a comparison of a processor that supports Intel HT Technology (implemented with two logical
processors) and a traditional dual processor system.
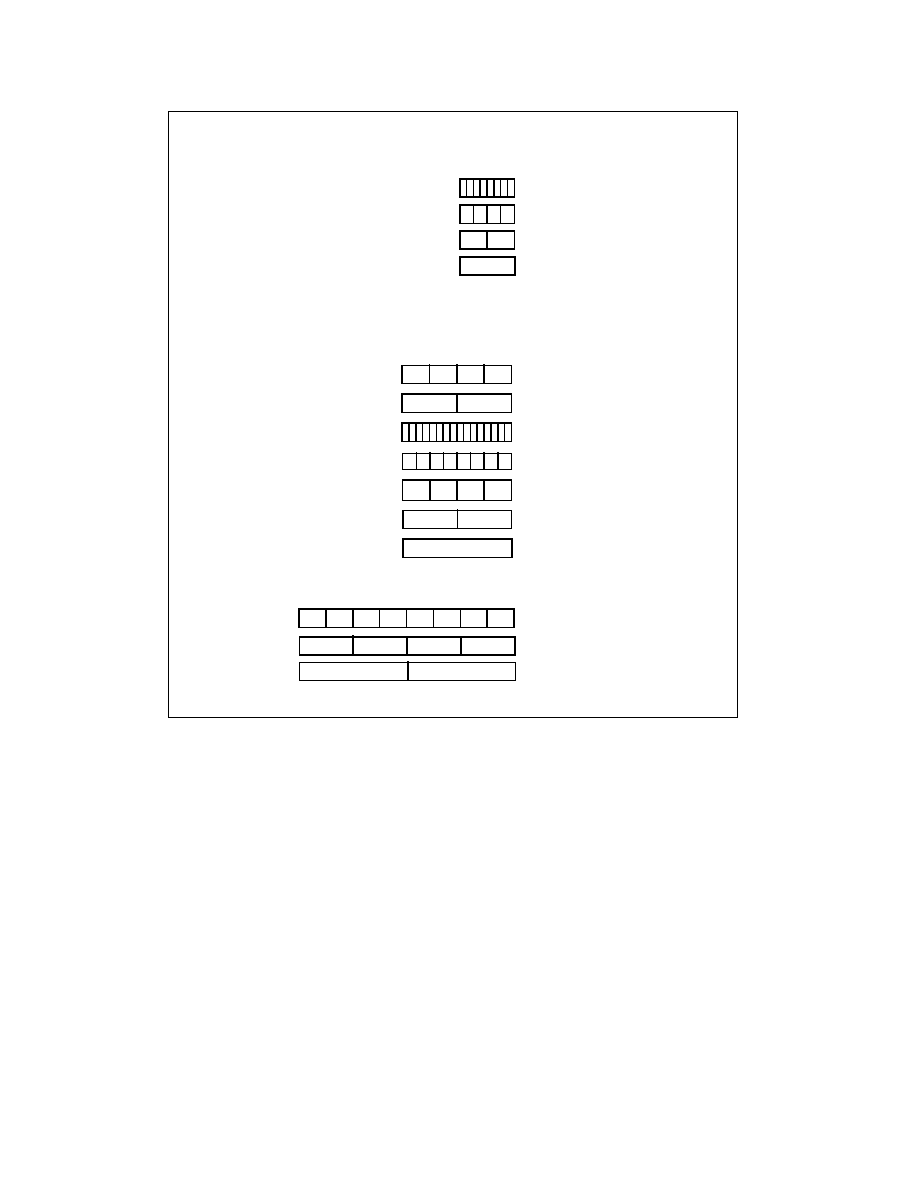
Figure 2-4. SIMD Extensions, Register Layouts, and Data Types
4 Packed Word Integers
8 Packed Byte Integers
2 Packed Doubleword Integers
MMX Registers
Quadword
MMX Technology - SSSE3
Data Type
Register Layout
SIMD Extension
SSE - AVX
4 Packed Single-Precision
Floating-Point Values
2 Packed Double-Precision
Floating-Point Values
8 Packed Word Integers
16 Packed Byte Integers
4 Packed Doubleword
2 Quadword Integers
Double Quadword
Integers
XMM Registers
8 Packed SP FP Values
4 Packed DP FP Values
YMM Registers
AVX
2 128-bit Data