2-18 Vol. 1
INTEL
®
64 AND IA-32 ARCHITECTURES
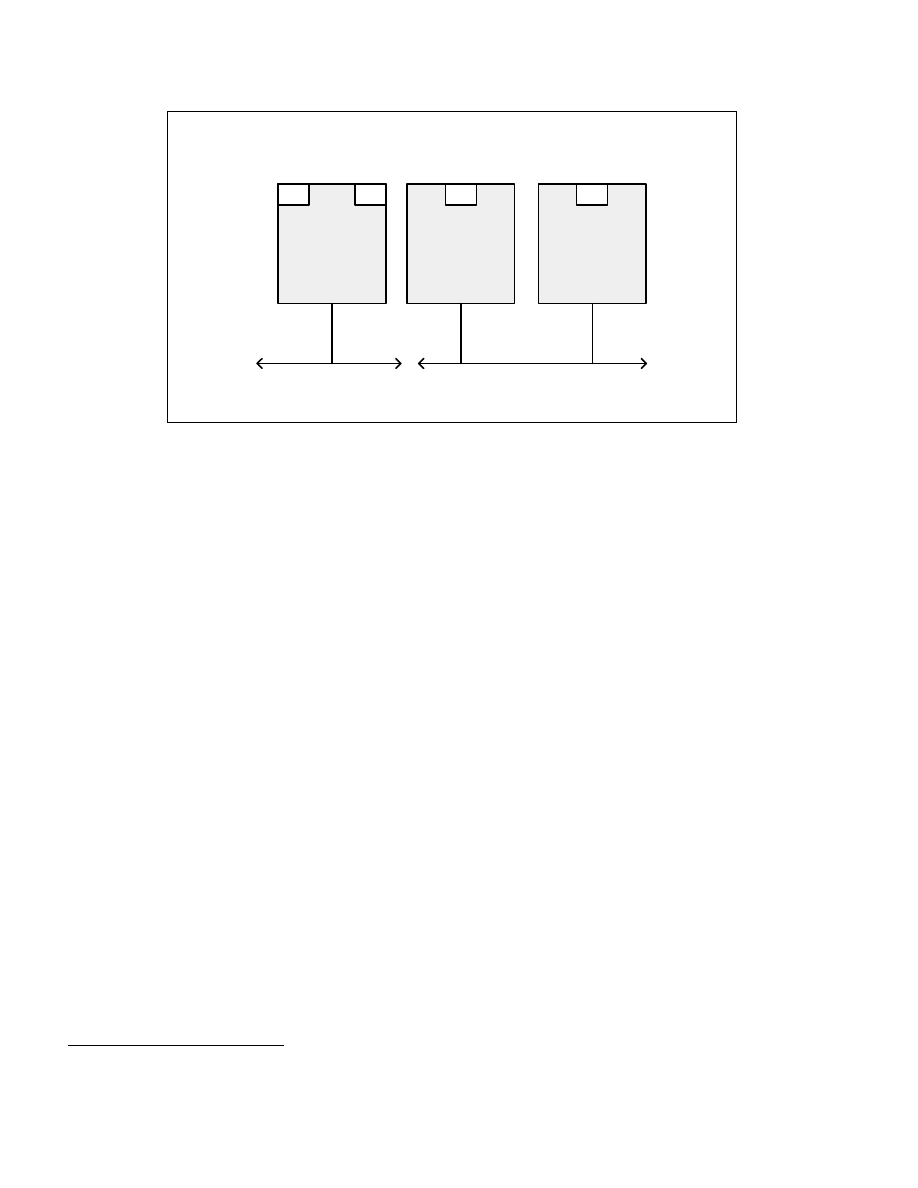
Unlike a traditional MP system configuration that uses two or more separate physical IA-32 processors, the logical
processors in an IA-32 processor supporting Intel HT Technology share the core resources of the physical
processor. This includes the execution engine and the system bus interface. After power up and initialization, each
logical processor can be independently directed to execute a specified thread, interrupted, or halted.
Intel HT Technology leverages the process and thread-level parallelism found in contemporary operating systems
and high-performance applications by providing two or more logical processors on a single chip. This configuration
allows two or more threads
1
to be executed simultaneously on each a physical processor. Each logical processor
executes instructions from an application thread using the resources in the processor core. The core executes these
threads concurrently, using out-of-order instruction scheduling to maximize the use of execution units during each
clock cycle.
2.2.8.1
Some Implementation Notes
All Intel HT Technology configurations require:
•
A processor that supports Intel HT Technology
•
A chipset and BIOS that utilize the technology
•
Operating system optimizations
See
http://www.intel.com/products/ht/hyperthreading_more.htm
for information.
At the firmware (BIOS) level, the basic procedures to initialize the logical processors in a processor supporting Intel
HT Technology are the same as those for a traditional DP or MP platform. The mechanisms that are described in the
Multiprocessor Specification, Version 1.4 to power-up and initialize physical processors in an MP system also apply
to logical processors in a processor that supports Intel HT Technology.
An operating system designed to run on a traditional DP or MP platform may use CPUID to determine the presence
of hardware multi-threading support feature and the number of logical processors they provide.
Although existing operating system and application code should run correctly on a processor that supports Intel HT
Technology, some code modifications are recommended to get the optimum benefit. These modifications are
discussed in Chapter 7, “Multiple-Processor Management,” Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s
Manual, Volume 3A.
Figure 2-5. Comparison of an IA-32 Processor Supporting Hyper-Threading Technology and a Traditional Dual
Processor System
1. In the remainder of this document, the term “thread” will be used as a general term for the terms “process” and “thread.”
Processor Core
Processor Core
Processor Core
AS
AS
AS
AS
Traditional Multiple Processor (MP) System
IA-32 Processor Supporting
Hyper-Threading Technology
AS = IA-32 Architectural State
IA-32 processor
IA-32 processor
Two logical
processors that share
a single core
Each processor is a
separate physical
package
IA-32 processor
OM16522