Vol. 1 12-11
PROGRAMMING WITH INTEL® SSE3, SSSE3, INTEL® SSE4 AND INTEL® AESNI
increase support for packed dword computation. The technology also provides a hint that can improve memory
throughput when reading from uncacheable WC memory type.
The 47 SSE4.1 instructions include:
•
Two instructions perform packed dword multiplies.
•
Two instructions perform floating-point dot products with input/output selects.
•
One instruction performs a load with a streaming hint.
•
Six instructions simplify packed blending.
•
Eight instructions expand support for packed integer MIN/MAX.
•
Four instructions support floating-point round with selectable rounding mode and precision exception override.
•
Seven instructions improve data insertion and extractions from XMM registers
•
Twelve instructions improve packed integer format conversions (sign and zero extensions).
•
One instruction improves SAD (sum absolute difference) generation for small block sizes.
•
One instruction aids horizontal searching operations.
•
One instruction improves masked comparisons.
•
One instruction adds qword packed equality comparisons.
•
One instruction adds dword packing with unsigned saturation.
The SSE4.2 instructions operating on XMM registers improve performance in the following areas:
•
String and text processing that can take advantage of single-instruction multiple-data programming
techniques.
•
A SIMD integer instruction that enhances the capability of the 128-bit integer SIMD capability in SSE4.1.
12.10 SSE4.1 INSTRUCTION SET
12.10.1 Dword Multiply Instructions
SSE4.1 adds two dword multiply instructions that aid vectorization. They allow four simultaneous 32 bit by 32 bit
multiplies. PMULLD returns a low 32-bits of the result and PMULDQ returns a 64-bit signed result. These represent
the most common integer multiply operation. See Table 12-2.
12.10.2 Floating-Point Dot Product Instructions
SSE4.1 adds two instructions for double-precision (for up to 2 elements; DPPD) and single-precision dot products
(for up to 4 elements; DPPS).
These dot-product instructions include source select and destination broadcast which generally improves the flex-
ibility. For example, a single DPPS instruction can be used for a 2, 3, or 4 element dot product.
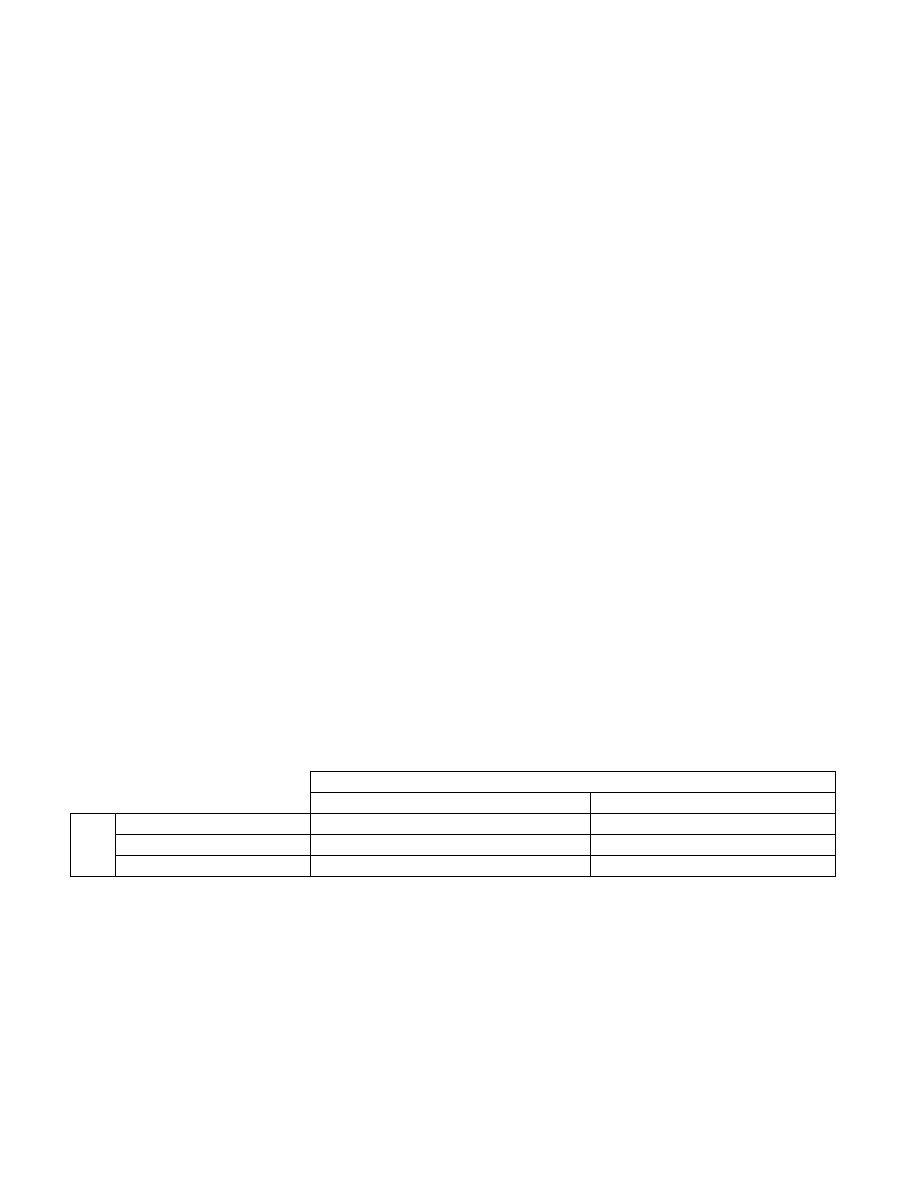
Table 12-2. Enhanced 32-bit SIMD Multiply Supported by SSE4.1
32 bit Integer Operation
unsigned x unsigned
signed x signed
Re
su
lt
Low 32-bit
(not available)
PMULLD
High 32-bit
(not available)
(not available)
64-bit
PMULUDQ*
PMULDQ
NOTE:
* Available prior to SSE4.1.