11-14 Vol. 1
PROGRAMMING WITH INTEL® STREAMING SIMD EXTENSIONS 2 (INTEL® SSE2)
point exception (#XM). If the OSXMMEXCEPT bit is clear, the processor generates an invalid-opcode exception
(#UD) on the first SSE or SSE2 instruction that detects a SIMD floating-point exception condition. See Section
11.6.2, “Checking for SSE/SSE2 Support.”
11.5.2
SIMD Floating-Point Exception Conditions
The following sections describe the conditions that cause a SIMD floating-point exception to be generated and the
masked response of the processor when these conditions are detected.
See Section 4.9.2, “Floating-Point Exception Priority,” for a description of the rules for exception precedence when
more than one floating-point exception condition is detected for an instruction.
11.5.2.1 Invalid Operation Exception (#I)
The floating-point invalid-operation exception (#I) occurs in response to an invalid arithmetic operand. The flag
(IE) and mask (IM) bits for the invalid operation exception are bits 0 and 7, respectively, in the MXCSR register.
If the invalid-operation exception is masked, the processor returns a QNaN, QNaN floating-point indefinite, integer
indefinite, one of the source operands to the destination operand, or it sets the EFLAGS, depending on the operation
being performed. When a value is returned to the destination operand, it overwrites the destination register specified
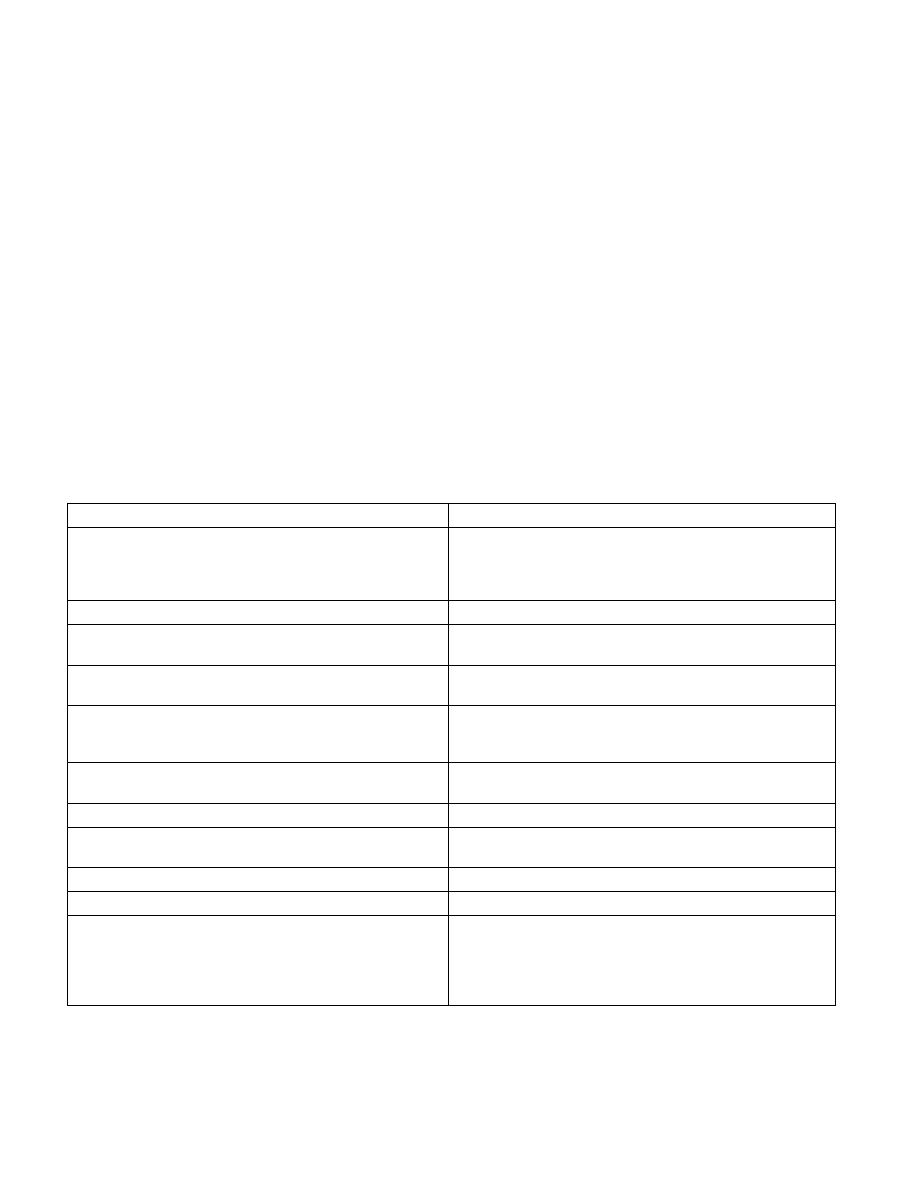
by the instruction. Table 11-1 lists the invalid-arithmetic operations that the processor detects for instructions and
the masked responses to these operations.
If the invalid operation exception is not masked, a software exception handler is invoked and the operands remain
unchanged. See Section 11.5.4, “Handling SIMD Floating-Point Exceptions in Software.”
Table 11-1. Masked Responses of SSE/SSE2/SSE3 Instructions to Invalid Arithmetic Operations
Condition
Masked Response
ADDPS, ADDSS, ADDPD, ADDSD, SUBPS, SUBSS, SUBPD, SUBSD,
MULPS, MULSS, MULPD, MULSD, DIVPS, DIVSS, DIVPD, DIVSD,
ADDSUBPD, ADDSUBPD, HADDPD, HADDPS, HSUBPD or HSUBPS
instruction with an SNaN operand
Return the SNaN converted to a QNaN; Refer to Table 4-7 for
more details
SQRTPS, SQRTSS, SQRTPD, or SQRTSD with SNaN operands
Return the SNaN converted to a QNaN
SQRTPS, SQRTSS, SQRTPD, or SQRTSD with negative operands
(except zero)
Return the QNaN floating-point Indefinite
MAXPS, MAXSS, MAXPD, MAXSD, MINPS, MINSS, MINPD, or
MINSD instruction with QNaN or SNaN operands
Return the source 2 operand value
CMPPS, CMPSS, CMPPD or CMPSD instruction with QNaN or SNaN
operands
Return a mask of all 0s (except for the predicates “not-equal,”
“unordered,” “not-less-than,” or “not-less-than-or-equal,” which
returns a mask of all 1s)
CVTPD2PS, CVTSD2SS, CVTPS2PD, CVTSS2SD with SNaN
operands
Return the SNaN converted to a QNaN
COMISS or COMISD with QNaN or SNaN operand(s)
Set EFLAGS values to “not comparable”
Addition of opposite signed infinities or subtraction of like-signed
infinities
Return the QNaN floating-point Indefinite
Multiplication of infinity by zero
Return the QNaN floating-point Indefinite
Divide of (0/0) or (
∞
/
∞
)
Return the QNaN floating-point Indefinite
Conversion to integer when the value in the source register is a
NaN,
∞
, or exceeds the representable range for CVTPS2PI,
CVTTPS2PI, CVTSS2SI, CVTTSS2SI, CVTPD2PI, CVTSD2SI,
CVTPD2DQ, CVTTPD2PI, CVTTSD2SI, CVTTPD2DQ, CVTPS2DQ,
or CVTTPS2DQ
Return the integer Indefinite