Vol. 1 10-7
PROGRAMMING WITH INTEL® STREAMING SIMD EXTENSIONS (INTEL® SSE)
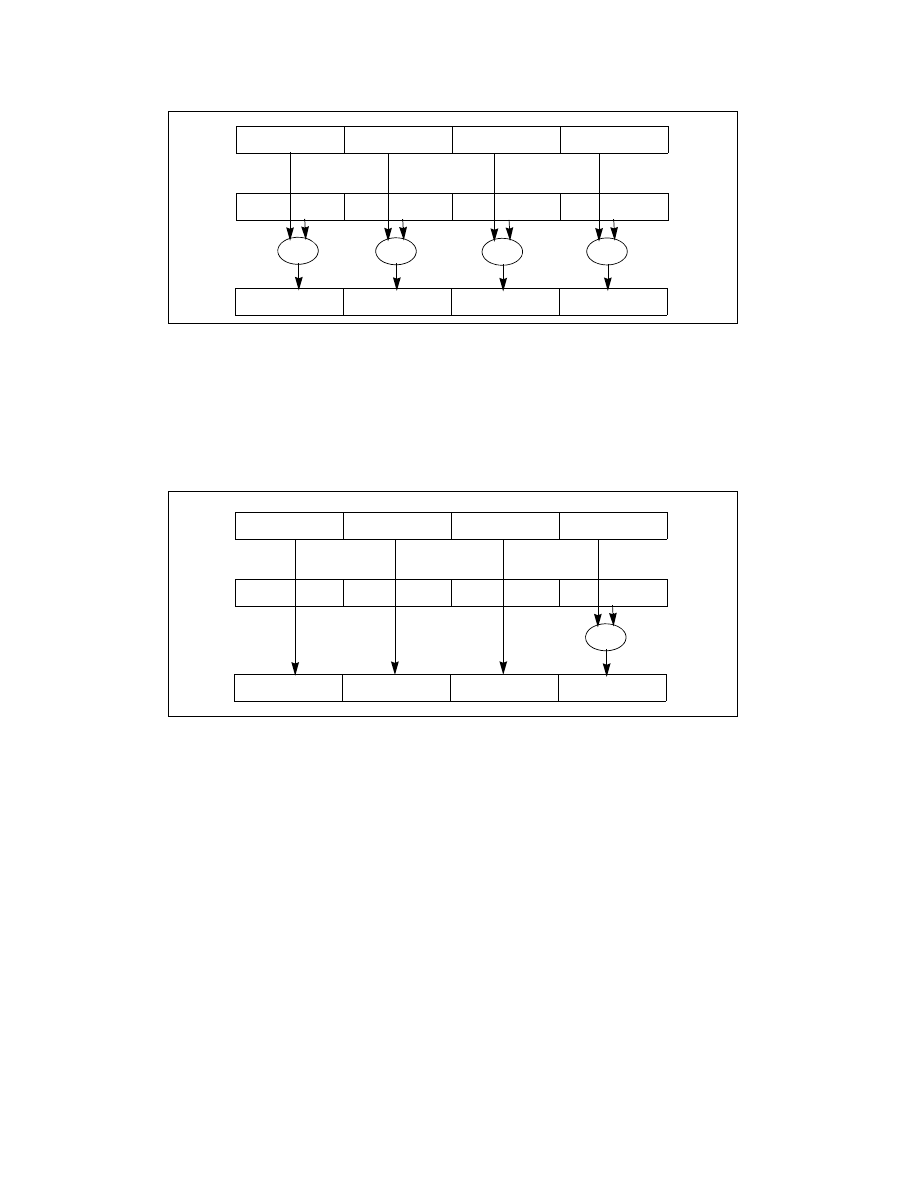
The scalar single-precision floating-point instructions operate on the low (least significant) doublewords of the two
source operands (X0 and Y0); see Figure 10-6. The three most significant doublewords (X1, X2, and X3) of the first
source operand are passed through to the destination. The scalar operations are similar to the floating-point oper-
ations performed in the x87 FPU data registers with the precision control field in the x87 FPU control word set for
single precision (24-bit significand), except that x87 stack operations use a 15-bit exponent range for the result,
while SSE operations use an 8-bit exponent range.
10.4.1.1 SSE Data Movement Instructions
SSE data movement instructions move single-precision floating-point data between XMM registers and between an
XMM register and memory.
The MOVAPS (move aligned packed single-precision floating-point values) instruction transfers a double quadword
operand containing four packed single-precision floating-point values from memory to an XMM register and vice
versa, or between XMM registers. The memory address must be aligned to a 16-byte boundary; otherwise, a
general-protection exception (#GP) is generated.
The MOVUPS (move unaligned packed single-precision, floating-point) instruction performs the same operations as
the MOVAPS instruction, except that 16-byte alignment of a memory address is not required.
The MOVSS (move scalar single-precision floating-point) instruction transfers a 32-bit single-precision floating-
point operand from memory to the low doubleword of an XMM register and vice versa, or between XMM registers.
The MOVLPS (move low packed single-precision floating-point) instruction moves two packed single-precision
floating-point values from memory to the low quadword of an XMM register and vice versa. The high quadword of
the register is left unchanged.
Figure 10-5. Packed Single-Precision Floating-Point Operation
Figure 10-6. Scalar Single-Precision Floating-Point Operation
X3
X2
X1
X0
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y0
X3 OP Y3
X2 OP Y2
X1 OP Y1
X0 OP Y0
OP
OP
OP
OP
X3
X2
X1
X0
Y3
Y2
Y1
Y0
X3
X2
X1
X0 OP Y0
OP