8-28 Vol. 1
PROGRAMMING WITH THE X87 FPU
tion operand and/or sets the floating-point condition codes as shown in Table 8-10. If the invalid-operation excep-
tion is not masked, a software exception handler is invoked (see Section 8.7, “Handling x87 FPU Exceptions in
Software”) and the top-of-stack pointer (TOP) and source operands remain unchanged.
Normally, when one or both of the source operands is a QNaN (and neither is an SNaN or in an unsupported
format), an invalid-operand exception is not generated. An exception to this rule is most of the compare instruc-
tions (such as the FCOM and FCOMI instructions) and the floating-point to integer conversion instructions
(FIST/FISTP and FBSTP). With these instructions, a QNaN source operand will generate an invalid-operand excep-
tion.
8.5.2
Denormal Operand Exception (#D)
The x87 FPU signals the denormal-operand exception under the following conditions:
•
If an arithmetic instruction attempts to operate on a denormal operand (see Section 4.8.3.2, “Normalized and
Denormalized Finite Numbers”).
•
If an attempt is made to load a denormal single-precision or double-precision floating-point value into an x87
FPU register. (If the denormal value being loaded is a double extended-precision floating-point value, the
denormal-operand exception is not reported.)
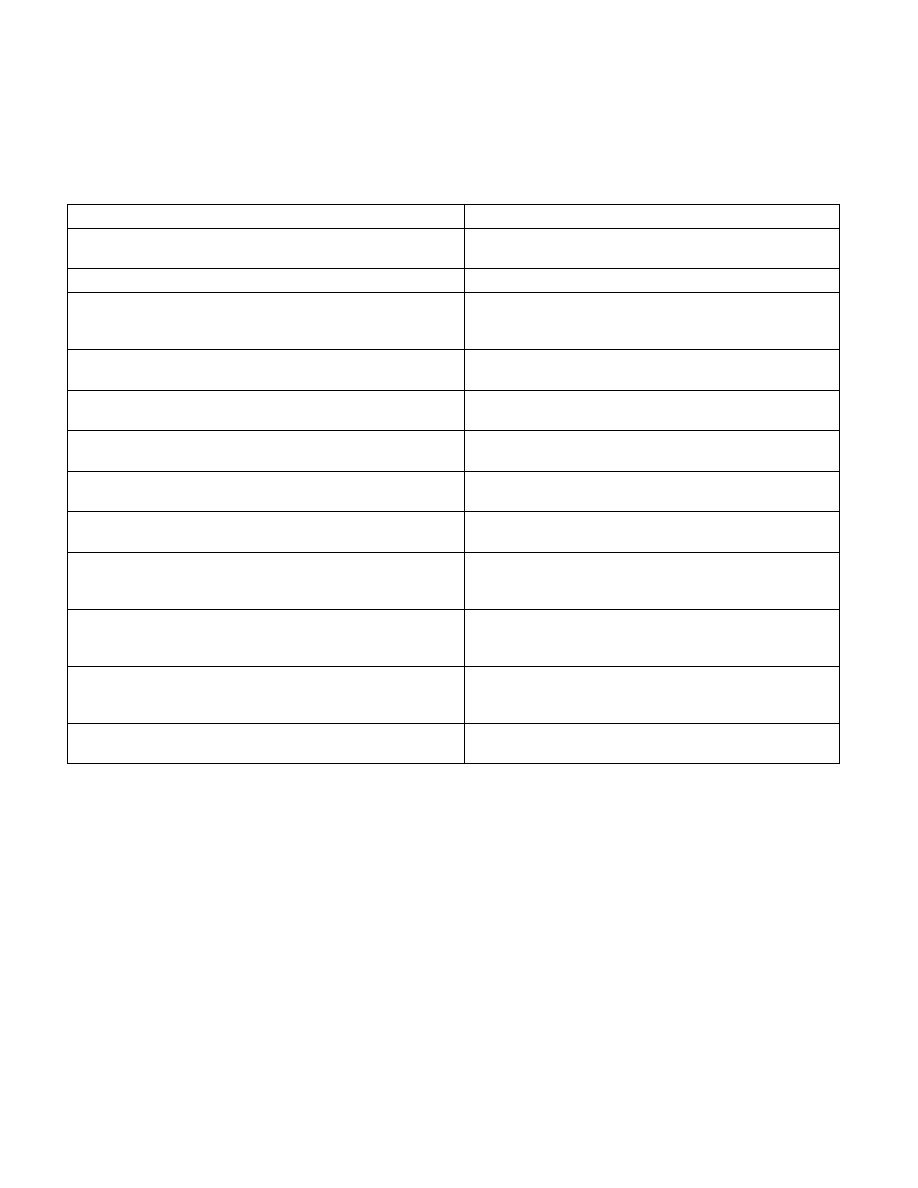
Table 8-10. Invalid Arithmetic Operations and the
Masked Responses to Them
Condition
Masked Response
Any arithmetic operation on an operand that is in an unsupported
format.
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite value to the
destination operand.
Any arithmetic operation on a SNaN.
Return a QNaN to the destination operand (see Table 4-7).
Ordered compare and test operations: one or both operands are
NaNs.
Set the condition code flags (C0, C2, and C3) in the x87 FPU
status word or the CF, PF, and ZF flags in the EFLAGS register to
111B (not comparable).
Addition: operands are opposite-signed infinities.
Subtraction: operands are like-signed infinities.
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite value to the
destination operand.
Multiplication: ∞ by 0; 0 by ∞ .
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite value to the
destination operand.
Division: ∞ by ∞ ; 0 by 0.
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite value to the
destination operand.
Remainder instructions FPREM, FPREM1: modulus (divisor) is 0 or
dividend is ∞ .
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite; clear condition code
flag C2 to 0.
Trigonometric instructions FCOS, FPTAN, FSIN, FSINCOS: source
operand is ∞ .
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite; clear condition code
flag C2 to 0.
FSQRT: negative operand (except FSQRT (–0) = –0); FYL2X: negative
operand (except FYL2X (–0) = –∞); FYL2XP1: operand more
negative than –1.
Return the QNaN floating-point indefinite value to the
destination operand.
FBSTP: Converted value cannot be represented in 18 decimal digits,
or source value is an SNaN, QNaN, ± ∞ , or in an unsupported
format.
Store packed BCD integer indefinite value in the destination
operand.
FIST/FISTP: Converted value exceeds representable integer range
of the destination operand, or source value is an SNaN, QNaN, ±∞,
or in an unsupported format.
Store integer indefinite value in the destination operand.
FXCH: one or both registers are tagged empty.
Load empty registers with the QNaN floating-point indefinite
value, then perform the exchange.