13-4 Vol. 3A
SYSTEM PROGRAMMING FOR INSTRUCTION SET EXTENSIONS AND PROCESSOR EXTENDED STATES
The SIMD floating-point exception mask bits (bits 7 through 12), the flush-to-zero flag (bit 15), the denormals-are-
zero flag (bit 6), and the rounding control field (bits 13 and 14) in the MXCSR register should be left in their default
values of 0. This permits the application to determine how these features are to be used.
13.1.4
Providing Non-Numeric Exception Handlers for Exceptions Generated by the SSE
Instructions
SSE instructions can generate the same type of memory-access exceptions (such as page faults and limit viola-
tions) and other non-numeric exceptions as other Intel 64 and IA-32 architecture instructions generate.
Ordinarily, existing exception handlers can handle these and other non-numeric exceptions without code modifica-
tion. However, depending on the mechanisms used in existing exception handlers, some modifications might need
to be made.
The SSE extensions can generate the non-numeric exceptions listed below:
•
Memory Access Exceptions:
— Stack-segment fault (#SS).
— General protection exception (#GP). Executing most SSE instructions with an unaligned 128-bit memory
reference generates a general-protection exception. (The MOVUPS and MOVUPD instructions allow
unaligned a loads or stores of 128-bit memory locations, without generating a general-protection
exception.) A 128-bit reference within the stack segment that is not aligned to a 16-byte boundary will also
generate a general-protection exception, instead a stack-segment fault exception (#SS).
— Page fault (#PF).
— Alignment check (#AC). When enabled, this type of alignment check operates on operands that are less
than 128-bits in size: 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit. To enable the generation of alignment check exceptions, do
the following:
•
Set the AM flag (bit 18 of control register CR0)
•
Set the AC flag (bit 18 of the EFLAGS register)
•
CPL must be 3
If alignment check exceptions are enabled, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit misalignment will be detected for the
MOVUPD and MOVUPS instructions; detection of 128-bit misalignment is not guaranteed and may vary
with implementation.
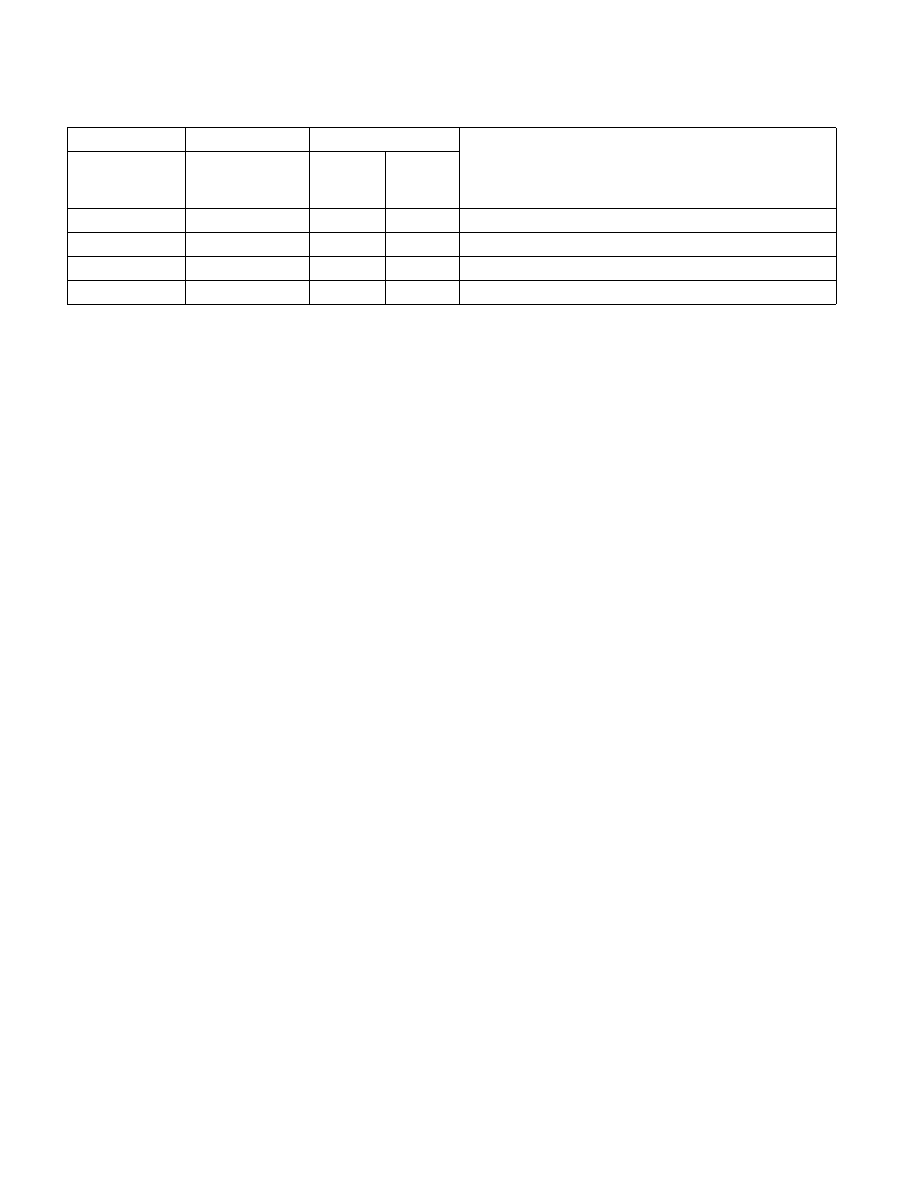
Table 13-2. Action Taken for Combinations of OSFXSR, SSSE3, SSE4, EM, and TS
CR4
CPUID
CR0 Flags
OSFXSR
SSSE3
SSE4_1
1
SSE4_2
2
NOTES:
1. Applies to SSE4_1 instructions except DPPS, DPPD, ROUNDPS, ROUNDPD, ROUNDSS, ROUNDSD.
2. Applies to SSE4_2 instructions except CRC32 and POPCNT.
EM
TS
Action
0
X
3
3. X = Don’t care.
X
X
#UD exception.
1
0
X
X
#UD exception.
1
1
1
X
#UD exception.
1
1
0
1
#NM exception.