11-12 Vol. 3A
MEMORY CACHE CONTROL
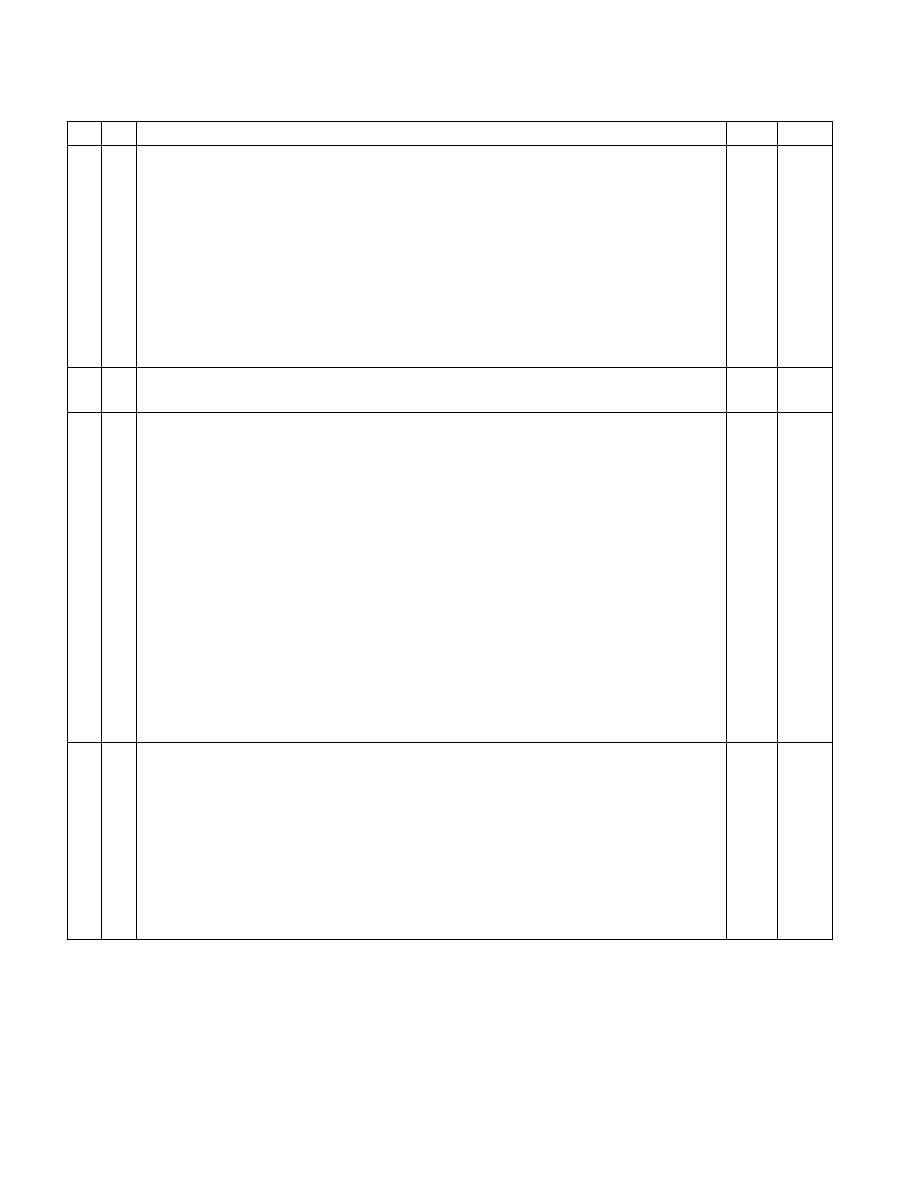
Table 11-5. Cache Operating Modes
CD NW
Caching and Read/Write Policy
L1
L2/L3
1
0
0
Normal Cache Mode. Highest performance cache operation.
• Read hits access the cache; read misses may cause replacement.
• Write hits update the cache.
• Only writes to shared lines and write misses update system memory.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
• Write misses cause cache line fills.
• Write hits can change shared lines to modified under control of the MTRRs and with associated
read invalidation cycle.
• (Pentium processor only.) Write misses do not cause cache line fills.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
• (Pentium processor only.) Write hits can change shared lines to exclusive under control of WB/WT#.
• Invalidation is allowed.
• External snoop traffic is supported.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
0
1
Invalid setting.
Generates a general-protection exception (#GP) with an error code of 0.
NA
NA
1
0
No-fill Cache Mode. Memory coherency is maintained.
3
• (Pentium 4 and later processor families.) State of processor after a power up or reset.
• Read hits access the cache; read misses do not cause replacement (see Pentium 4 and Intel Xeon
processors reference below).
• Write hits update the cache.
• Only writes to shared lines and write misses update system memory.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
• Write misses access memory.
• Write hits can change shared lines to exclusive under control of the MTRRs and with associated
read invalidation cycle.
• (Pentium processor only.) Write hits can change shared lines to exclusive under control of the
WB/WT#.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
• (P6 and later processor families only.) Strict memory ordering is not enforced unless the MTRRs are
disabled and/or all memory is referenced as uncached (see Section 7.2.4., “Strengthening or
Weakening the Memory Ordering Model”).
• Invalidation is allowed.
• External snoop traffic is supported.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1
1
Memory coherency is not maintained.
2, 3
• (P6 family and Pentium processors.) State of the processor after a power up or reset.
• Read hits access the cache; read misses do not cause replacement.
• Write hits update the cache and change exclusive lines to modified.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
• Shared lines remain shared after write hit.
• Write misses access memory.
• Invalidation is inhibited when snooping; but is allowed with INVD and WBINVD instructions.
• External snoop traffic is supported.
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
NOTES:
1. The L2/L3 column in this table is definitive for the Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 family processors. It is intended to represent what
could be implemented in a system based on a Pentium processor with an external, platform specific, write-back L2 cache.
2. The Pentium 4 and more recent processor families do not support this mode; setting the CD and NW bits to 1 selects the no-fill
cache mode.
3. Not supported In Intel Atom processors. If CD = 1 in an Intel Atom processor, caching is disabled.