9-16 Vol. 3A
PROCESSOR MANAGEMENT AND INITIALIZATION
9.10.1 Assembler
Usage
In this example, the Intel assembler ASM386 and build tools BLD386 are used to assemble and build the initializa-
tion code module. The following assumptions are used when using the Intel ASM386 and BLD386 tools.
•
The ASM386 will generate the right operand size opcodes according to the code-segment attribute. The
attribute is assigned either by the ASM386 invocation controls or in the code-segment definition.
•
If a code segment that is going to run in real-address mode is defined, it must be set to a USE 16 attribute. If
a 32-bit operand is used in an instruction in this code segment (for example, MOV EAX, EBX), the assembler
automatically generates an operand prefix for the instruction that forces the processor to execute a 32-bit
operation, even though its default code-segment attribute is 16-bit.
•
Intel's ASM386 assembler allows specific use of the 16- or 32-bit instructions, for example, LGDTW, LGDTD,
IRETD. If the generic instruction LGDT is used, the default- segment attribute will be used to generate the right
opcode.
9.10.2 STARTUP.ASM
Listing
Example 9-1 provides high-level sample code designed to move the processor into protected mode. This listing
does not include any opcode and offset information.
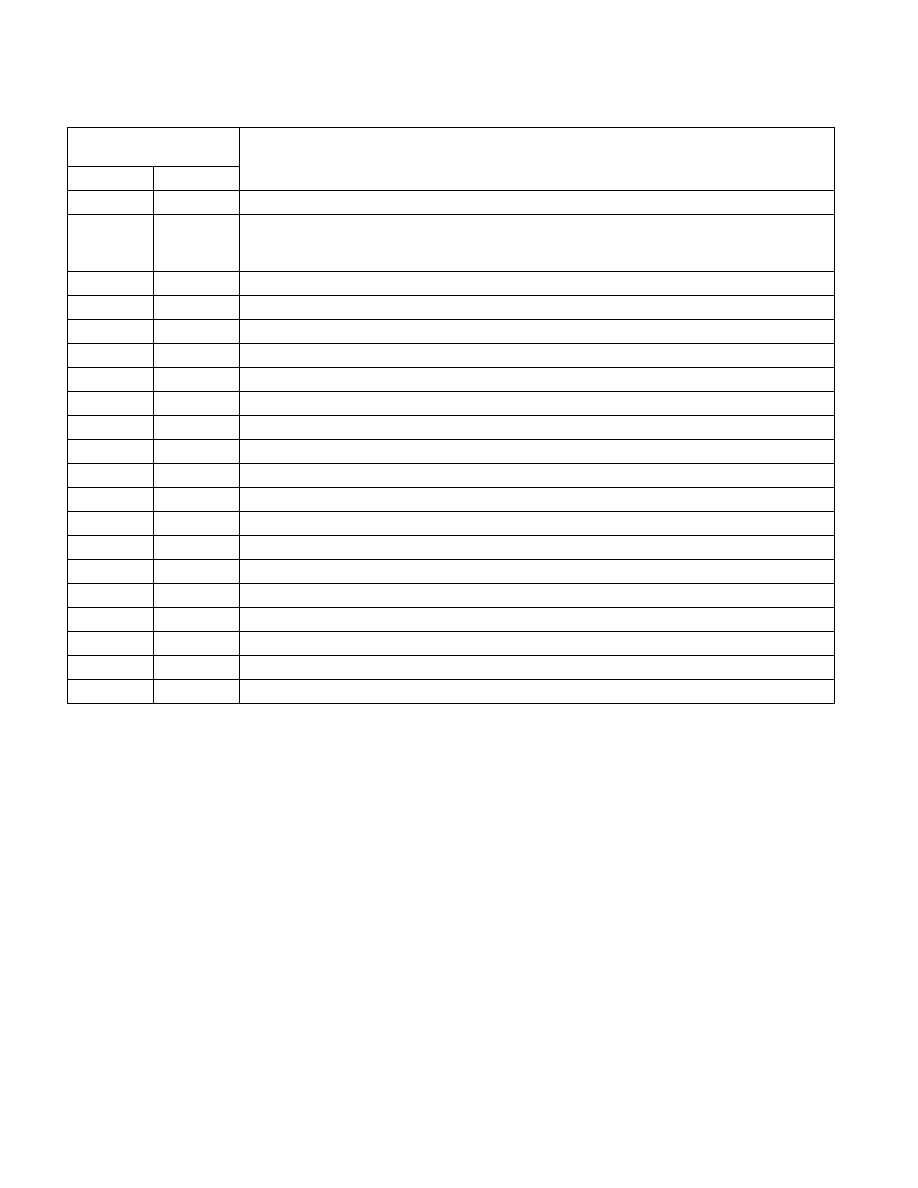
Table 9-5. Main Initialization Steps in STARTUP.ASM Source Listing
STARTUP.ASM Line
Numbers
Description
From
To
157
157
Jump (short) to the entry code in the EPROM
162
169
Construct a temporary GDT in RAM with one entry:
0 - null
1 - R/W data segment, base = 0, limit = 4 GBytes
171
172
Load the GDTR to point to the temporary GDT
174
177
Load CR0 with PE flag set to switch to protected mode
179
181
Jump near to clear real mode instruction queue
184
186
Load DS, ES registers with GDT[1] descriptor, so both point to the entire physical memory space
188
195
Perform specific board initialization that is imposed by the new protected mode
196
218
Copy the application's GDT from ROM into RAM
220
238
Copy the application's IDT from ROM into RAM
241
243
Load application's GDTR
244
245
Load application's IDTR
247
261
Copy the application's TSS from ROM into RAM
263
267
Update TSS descriptor and other aliases in GDT (GDT alias or IDT alias)
277
277
Load the task register (without task switch) using LTR instruction
282
286
Load SS, ESP with the value found in the application's TSS
287
287
Push EFLAGS value found in the application's TSS
288
288
Push CS value found in the application's TSS
289
289
Push EIP value found in the application's TSS
290
293
Load DS, ES with the value found in the application's TSS
296
296
Perform IRET; pop the above values and enter the application code