6-12 Vol. 3A
INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION HANDLING
When the processor performs a call to the exception- or interrupt-handler procedure:
•
If the handler procedure is going to be executed at a numerically lower privilege level, a stack switch occurs.
When the stack switch occurs:
a. The segment selector and stack pointer for the stack to be used by the handler are obtained from the TSS
for the currently executing task. On this new stack, the processor pushes the stack segment selector and
stack pointer of the interrupted procedure.
b. The processor then saves the current state of the EFLAGS, CS, and EIP registers on the new stack (see
c. If an exception causes an error code to be saved, it is pushed on the new stack after the EIP value.
•
If the handler procedure is going to be executed at the same privilege level as the interrupted procedure:
a. The processor saves the current state of the EFLAGS, CS, and EIP registers on the current stack (see
b. If an exception causes an error code to be saved, it is pushed on the current stack after the EIP value.
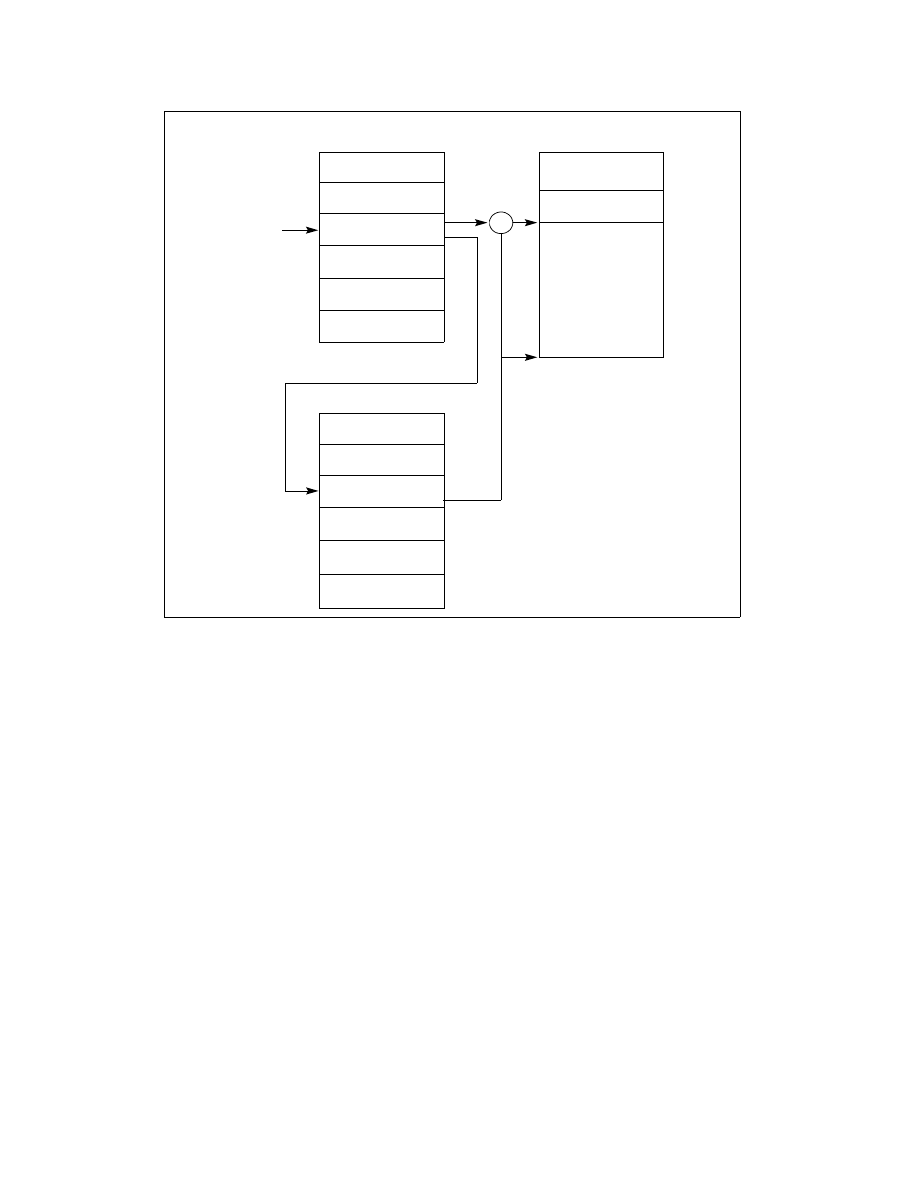
Figure 6-3. Interrupt Procedure Call
IDT
Interrupt or
Code Segment
Segment Selector
GDT or LDT
Segment
Interrupt
Vector
Base
Address
Destination
Procedure
Interrupt
+
Descriptor
Trap Gate
Offset