28-8 Vol. 3C
VMX SUPPORT FOR ADDRESS TRANSLATION
— A reserved bit is set. This includes the setting of a bit in the range 51:12 that is beyond the logical
processor’s physical-address width.
1
See Section 28.2.2 for details of which bits are reserved in which EPT
paging-structure entries.
— The entry is the last one used to translate a guest physical address (either an EPT PDE with bit 7 set to 1 or
an EPT PTE) and the value of bits 5:3 (EPT memory type) is 2, 3, or 7 (these values are reserved).
EPT misconfigurations result when an EPT paging-structure entry is configured with settings reserved for future
functionality. Software developers should be aware that such settings may be used in the future and that an EPT
paging-structure entry that causes an EPT misconfiguration on one processor might not do so in the future.
28.2.3.2 EPT Violations
An EPT violation may occur during an access using a guest-physical address whose translation does not cause an
EPT misconfiguration. An EPT violation occurs in any of the following situations:
•
Translation of the guest-physical address encounters an EPT paging-structure entry that is not present (see
Section 28.2.2).
•
The access is a data read and bit 0 was clear in any of the EPT paging-structure entries used to translate the
guest-physical address. Reads by the logical processor of guest paging structures to translate a linear address
are considered to be data reads.
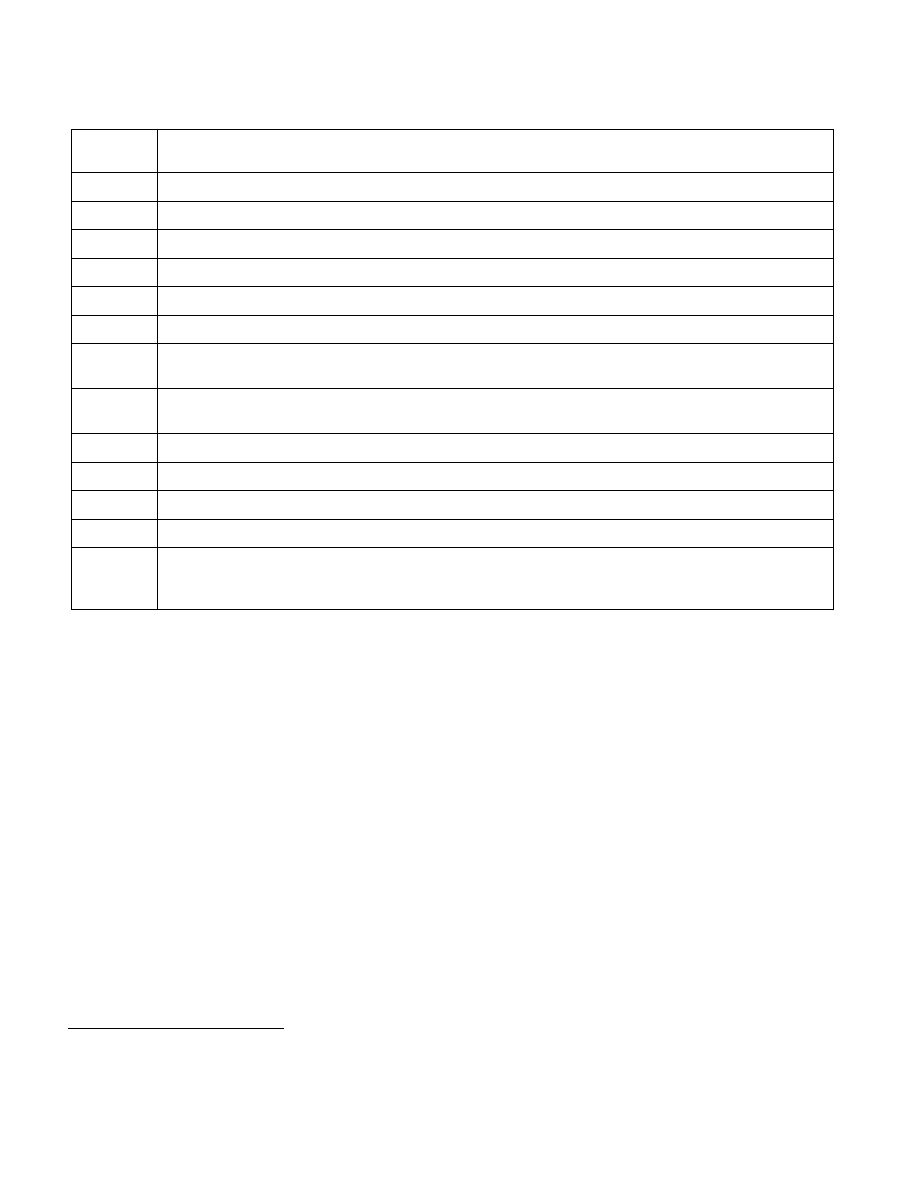
Table 28-6. Format of an EPT Page-Table Entry that Maps a 4-KByte Page
Bit
Position(s)
Contents
0
Read access; indicates whether reads are allowed from the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry
1
Write access; indicates whether writes are allowed to the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry
2
Execute access; indicates whether instruction fetches are allowed from the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry
5:3
EPT memory type for this 4-KByte page (see Section 28.2.6)
6
Ignore PAT memory type for this 4-KByte page (see Section 28.2.6)
7
Ignored
8
If bit 6 of EPTP is 1, accessed flag for EPT; indicates whether software has accessed the 4-KByte page referenced
by this entry (see Section 28.2.4). Ignored if bit 6 of EPTP is 0
9
If bit 6 of EPTP is 1, dirty flag for EPT; indicates whether software has written to the 4-KByte page referenced by
this entry (see Section 28.2.4). Ignored if bit 6 of EPTP is 0
11:10
Ignored
(N–1):12
Physical address of the 4-KByte page referenced by this entry
1
51:N
Reserved (must be 0)
62:52
Ignored
63
Suppress #VE. If the “EPT-violation #VE” VM-execution control is 1, EPT violations caused by accesses to this page
are convertible to virtualization exceptions only if this bit is 0 (see Section 25.5.6.1). If “EPT-violation #VE” VM-
execution control is 0, this bit is ignored.
NOTES:
1. N is the physical-address width supported by the logical processor.
1. Software can determine a processor’s physical-address width by executing CPUID with 80000008H in EAX. The physical-address
width is returned in bits 7:0 of EAX.