2-20 Vol. 2A
INSTRUCTION FORMAT
if XSAVE and XRSTOR are used with a save/restore mask that does not set bits corresponding to all supported
extensions to the vector registers.)
2.3.11
AVX Instruction Length
The AVX instructions described in this document (including VEX and ignoring other prefixes) do not exceed 11
bytes in length, but may increase in the future. The maximum length of an Intel 64 and IA-32 instruction remains
15 bytes.
2.3.12
Vector SIB (VSIB) Memory Addressing
In Intel
®
Advanced Vector Extensions 2 (Intel
®
AVX2), an SIB byte that follows the ModR/M byte can support VSIB
memory addressing to an array of linear addresses. VSIB addressing is only supported in a subset of Intel AVX2
instructions. VSIB memory addressing requires 32-bit or 64-bit effective address. In 32-bit mode, VSIB addressing
is not supported when address size attribute is overridden to 16 bits. In 16-bit protected mode, VSIB memory
addressing is permitted if address size attribute is overridden to 32 bits. Additionally, VSIB memory addressing is
supported only with VEX prefix.
In VSIB memory addressing, the SIB byte consists of:
•
The scale field (bit 7:6) specifies the scale factor.
•
The index field (bits 5:3) specifies the register number of the vector index register, each element in the vector
register specifies an index.
•
The base field (bits 2:0) specifies the register number of the base register.
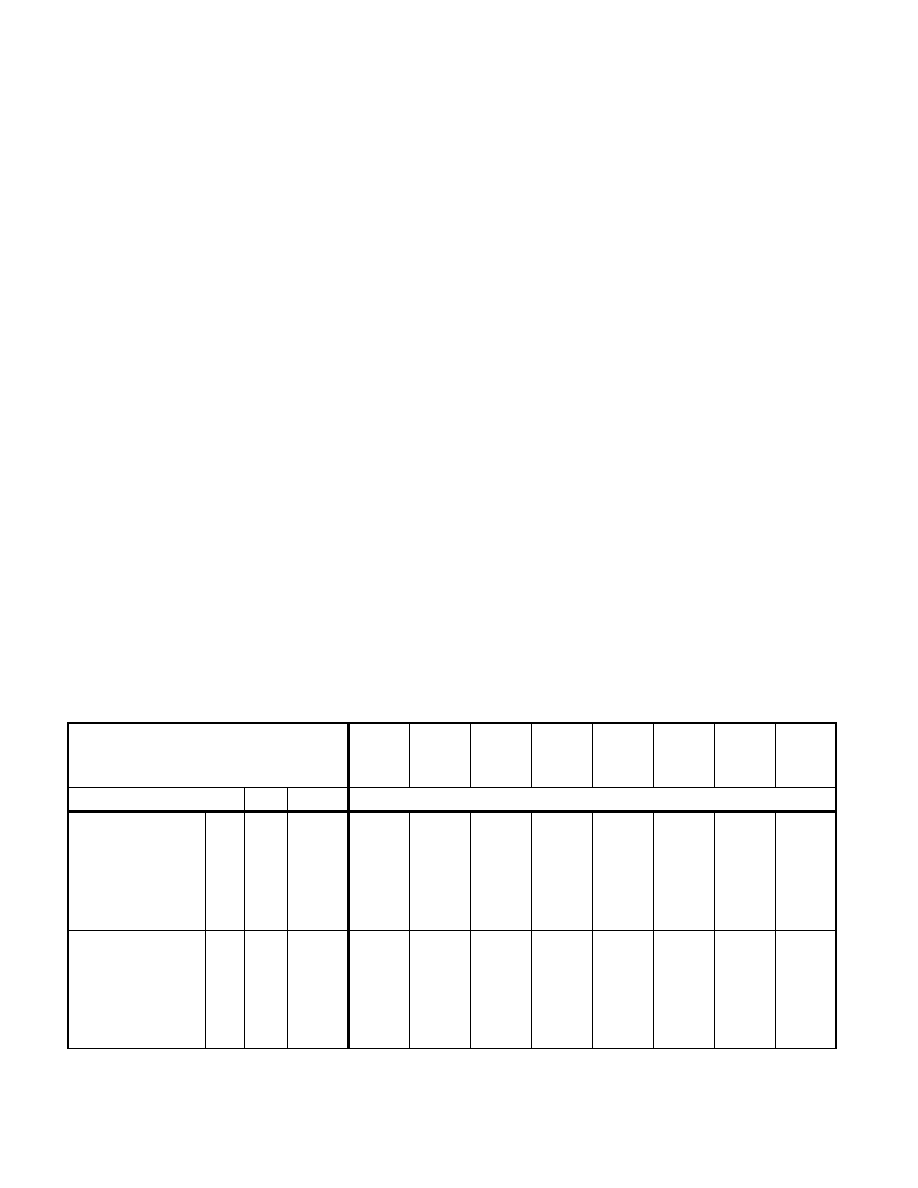
Table 2-3 shows the 32-bit VSIB addressing form. It is organized to give 256 possible values of the SIB byte (in
hexadecimal). General purpose registers used as a base are indicated across the top of the table, along with corre-
sponding values for the SIB byte’s base field. The register names also include R8L-R15L applicable only in 64-bit
mode (when address size override prefix is used, but the value of VEX.B is not shown in Table 2-3). In 32-bit mode,
R8L-R15L does not apply.
Table rows in the body of the table indicate the vector index register used as the index field and each supported
scaling factor shown separately. Vector registers used in the index field can be XMM or YMM registers. The left-
most column includes vector registers VR8-VR15 (i.e. XMM8/YMM8-XMM15/YMM15), which are only available in
64-bit mode and does not apply if encoding in 32-bit mode.
Table 2-13. 32-Bit VSIB Addressing Forms of the SIB Byte
r32
(In decimal) Base =
(In binary) Base =
EAX/
R8L
0
000
ECX/
R9L
1
001
EDX/
R10L
2
010
EBX/
R11L
3
011
ESP/
R12L
4
100
EBP/
R13L
1
5
101
ESI/
R14L
6
110
EDI/
R15L
7
111
Scaled Index
SS
Index
Value of SIB Byte (in Hexadecimal)
VR0/VR8
VR1/VR9
VR2/VR10
VR3/VR11
VR4/VR12
VR5/VR13
VR6/VR14
VR7/VR15
*1
00
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
00
08
10
18
20
28
30
38
01
09
11
19
21
29
31
39
02
0A
12
1A
22
2A
32
3A
03
0B
13
1B
23
2B
33
3B
04
0C
14
1C
24
2C
34
3C
05
0D
15
1D
25
2D
35
3D
06
0E
16
1E
26
2E
36
3E
07
0F
17
1F
27
2F
37
3F
VR0/VR8
VR1/VR9
VR2/VR10
VR3/VR11
VR4/VR12
VR5/VR13
VR6/VR14
VR7/VR15
*2
01
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
40
48
50
58
60
68
70
78
41
49
51
59
61
69
71
79
42
4A
52
5A
62
6A
72
7A
43
4B
53
5B
63
6B
73
7B
44
4C
54
5C
64
6C
74
7C
45
4D
55
5D
65
6D
75
7D
46
4E
56
5E
66
6E
76
7E
47
4F
57
5F
67
6F
77
7F