4-2 Vol. 1
DATA TYPES
4.1.1
Alignment of Words, Doublewords, Quadwords, and Double Quadwords
Words, doublewords, and quadwords do not need to be aligned in memory on natural boundaries. The natural
boundaries for words, double words, and quadwords are even-numbered addresses, addresses evenly divisible by
four, and addresses evenly divisible by eight, respectively. However, to improve the performance of programs, data
structures (especially stacks) should be aligned on natural boundaries whenever possible. The reason for this is
that the processor requires two memory accesses to make an unaligned memory access; aligned accesses require
only one memory access. A word or doubleword operand that crosses a 4-byte boundary or a quadword operand
that crosses an 8-byte boundary is considered unaligned and requires two separate memory bus cycles for access.
Some instructions that operate on double quadwords require memory operands to be aligned on a natural
boundary. These instructions generate a general-protection exception (#GP) if an unaligned operand is specified.
A natural boundary for a double quadword is any address evenly divisible by 16. Other instructions that operate on
double quadwords permit unaligned access (without generating a general-protection exception). However, addi-
tional memory bus cycles are required to access unaligned data from memory.
4.2 NUMERIC
DATA
TYPES
Although bytes, words, and doublewords are fundamental data types, some instructions support additional inter-
pretations of these data types to allow operations to be performed on numeric data types (signed and unsigned
integers, and floating-point numbers). Single-precision (32-bit) floating-point and double-precision (64-bit)
floating-point data types are supported across all generations of SSE extensions and Intel AVX extensions. Half-
precision (16-bit) floating-point data type is supported only with F16C extensions (VCVTPH2PS, VCVTPS2PH). See
Figure 4-3.
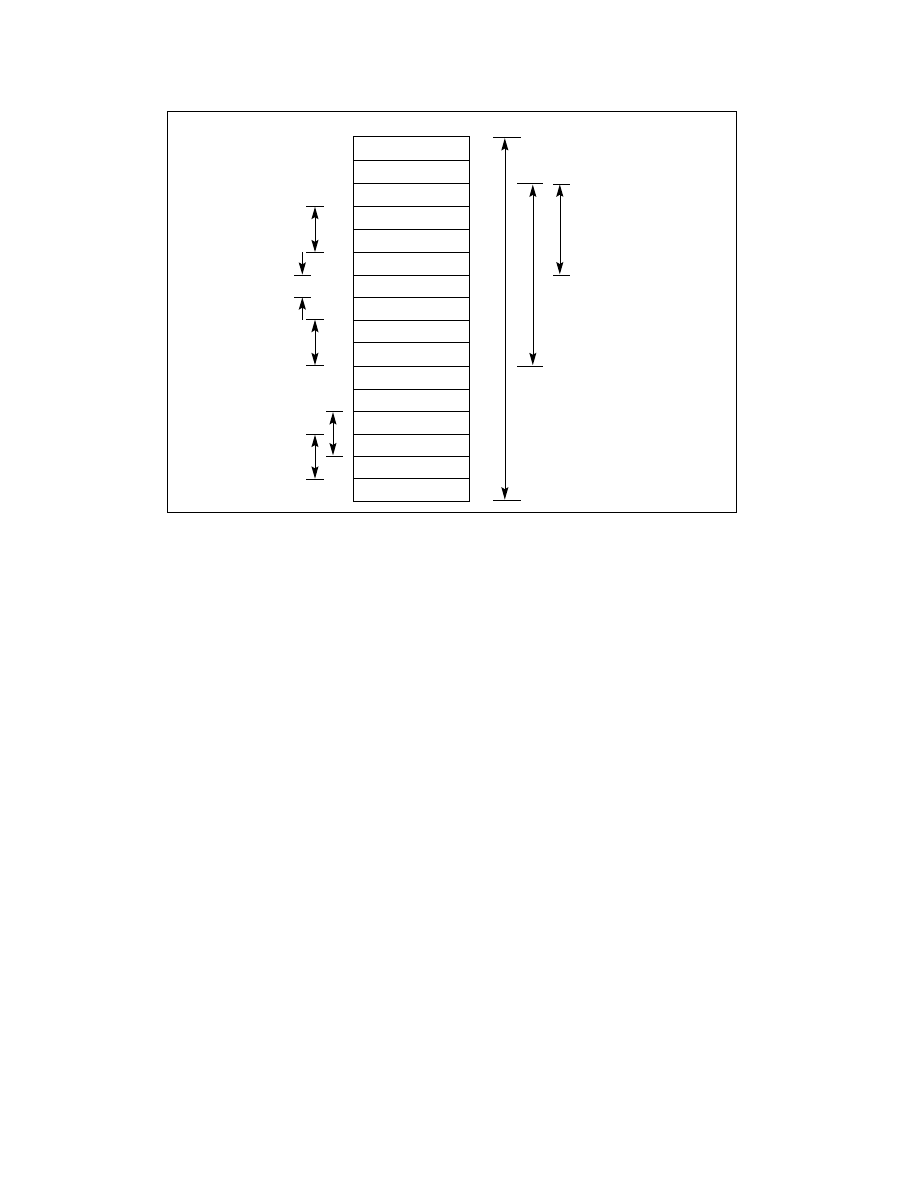
Figure 4-2. Bytes, Words, Doublewords, Quadwords, and Double Quadwords in Memory
EH
DH
7AH
CH
FEH
BH
06H
AH
36H
9H
1FH
8H
A4H
7H
23H
6H
0BH
5H
4H
3H
74H
2H
CBH
1H
31H
0H
Quadword at Address 6H
Contains
Doubleword at Address AH
Contains 7AFE0636H
Word at Address BH
Contains FE06H
Byte at Address 9H
Contains 1FH
Word at Address 6H
Contains 230BH
Word at Address 1H
Contains CB31H
Word at Address 2H
Contains 74CBH
Double quadword at Address 0H
45H
67H
12H
Contains
12H
7AFE06361FA4230BH
4E127AFE06361FA4230B456774CB3112
4EH
FH